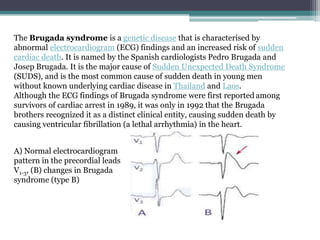
Bangungot, also known as sudden unexpected death syndrome (SUDS), refers to sudden unexpected death during sleep, particularly in adolescents and adults. It has been linked to genetic mutations affecting the cardiac sodium channel and can run in families. The condition is characterized by abnormal electrocardiogram readings and an increased risk of ventricular fibrillation leading to sudden cardiac death. The Brugada syndrome is a genetic cause of SUDS defined by distinct electrocardiogram changes and is the most common cause of sudden death in young men in Thailand and Laos without known heart disease.