Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times




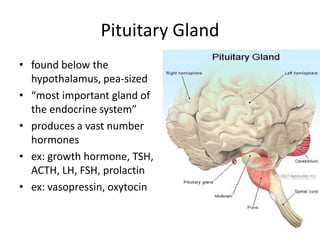







The endocrine system communicates through hormones secreted by various glands to control body functions. The major glands include the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain, the thyroid and parathyroid glands in the neck, the adrenal glands on the kidneys, the pineal gland in the brain, and cells in the pancreas and reproductive organs. Hormones regulate processes like metabolism, growth, mood, stress response, and calcium levels without connecting ducts by circulating in the bloodstream to target tissues.










