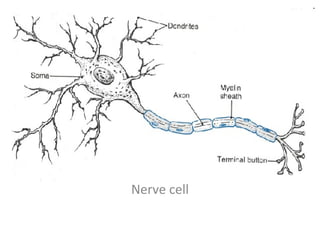
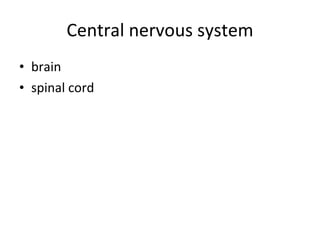
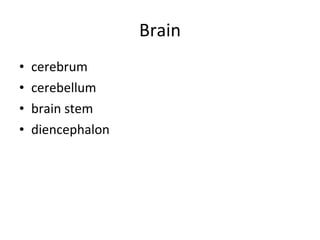
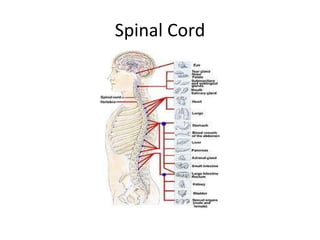
The nervous system has several key functions including controlling the respiratory center and relaying information about stimuli like pain, hunger, and full bladders. The nervous system receives information through nerve cells, interprets it, and causes the body to respond. Nerve cells are made up of dendrites that receive stimuli, an axon that carries impulses, and a nucleus. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and peripheral nerves. The autonomic nervous system has sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions that control involuntary functions.