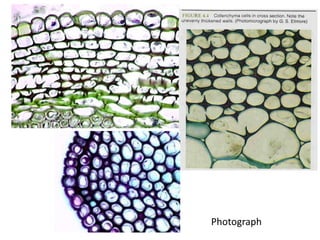
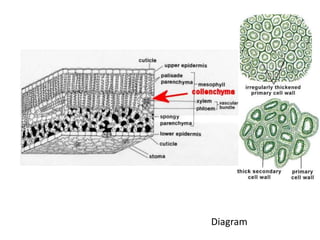
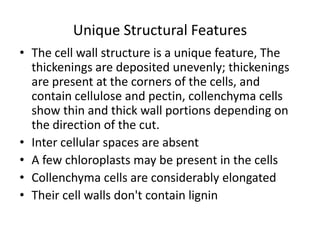
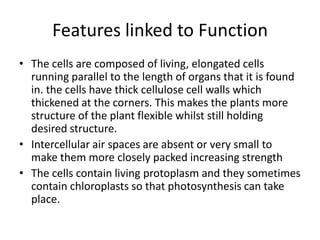
Collenchyma is a mechanical tissue found under the epidermis of young stems and in the veins of leaves. It provides support to growing organs through thick, unevenly thickened cell walls that are flexible due to being composed of cellulose and pectin instead of lignin. Collenchyma cells are elongated and closely packed without intercellular spaces, giving strength and structure while allowing growth through flexibility and elongation of the living cells.