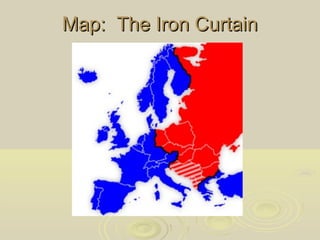
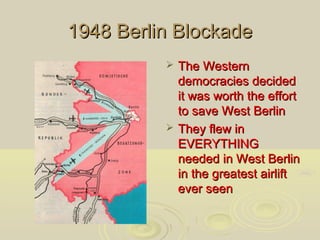
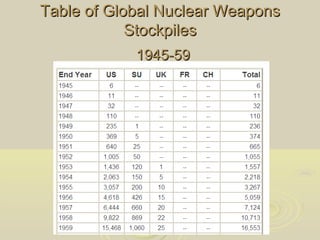
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and its allies, and the Soviet Union and its allies from 1945 to 1991. While direct military conflict was avoided, both sides amassed large stockpiles of nuclear weapons and engaged in espionage and proxy wars. Key events that heightened tensions included the Berlin Blockade, the formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, and the Soviet Union developing nuclear weapons in 1949. The threat of nuclear war cast a shadow over international relations for decades.