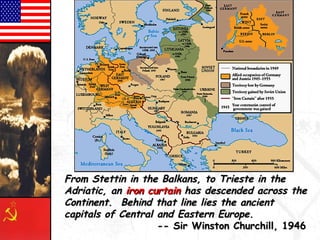
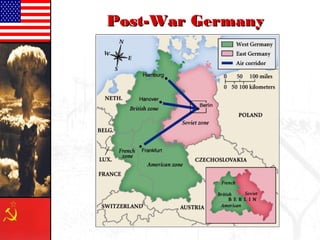
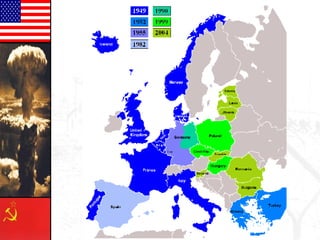
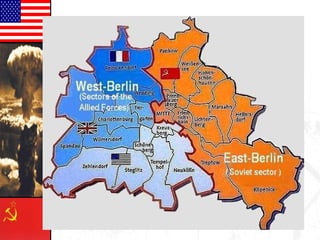
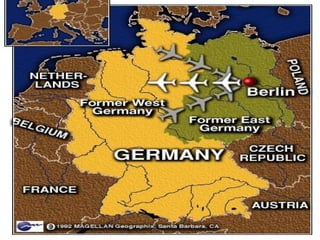
The document provides background information on the origins and early events of the Cold War between the Western nations led by the United States and the Eastern bloc nations dominated by the Soviet Union. It describes how tensions grew after World War II as the Soviets established control over Eastern Europe and divided Germany into East and West. This division of influence across Europe between the two superpowers led to the formation of opposing military alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact and set the stage for the global ideological conflict known as the Cold War.