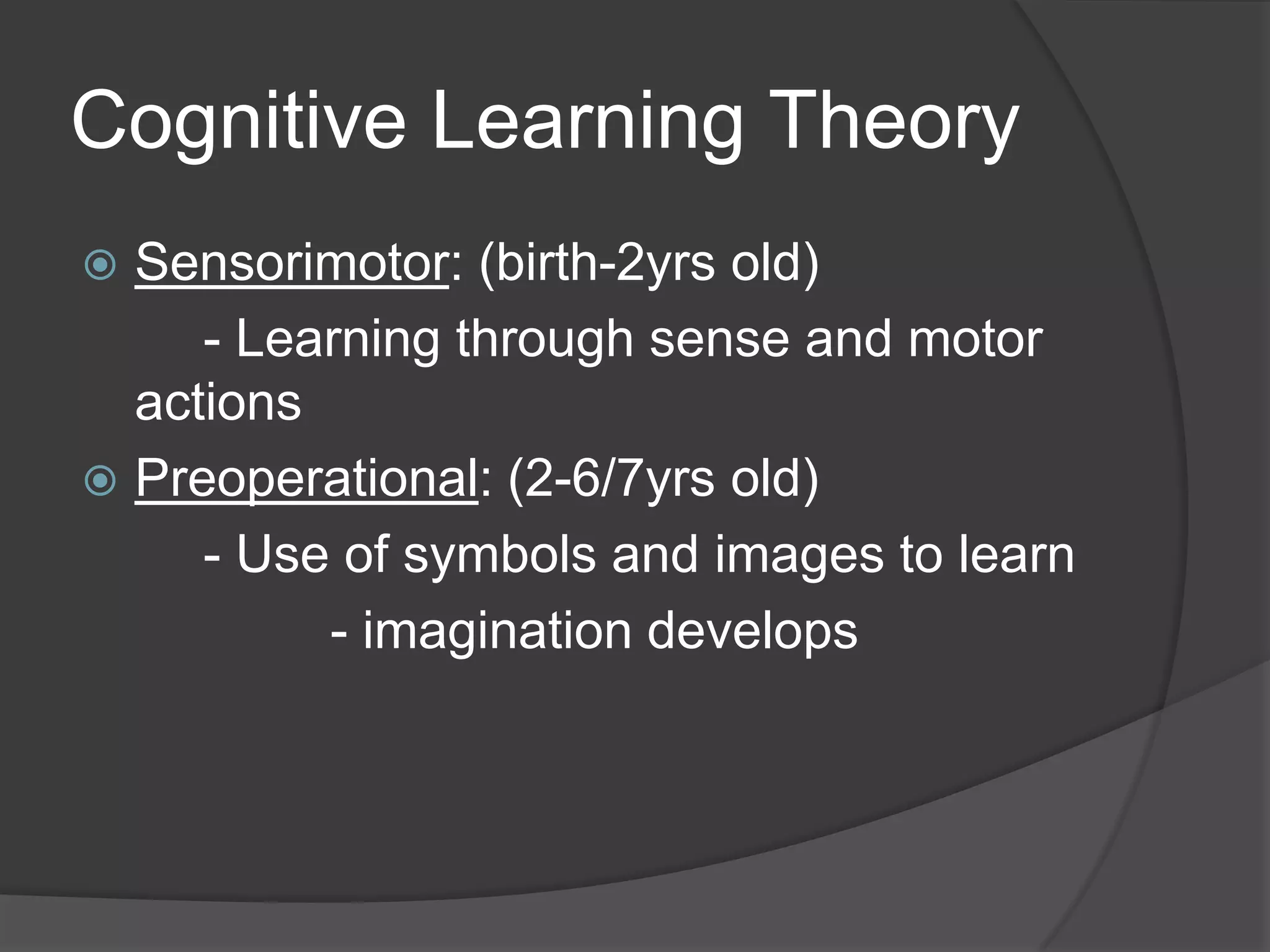
Cognitivism replaced behaviorism in the 1960s and focuses on understanding mental processes. Jean Piaget developed the central thesis that children are active learners who develop self-centric theories about their environment based on personal interactions and schemes. Piaget proposed four stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. During development, children adapt, assimilate, and accommodate new knowledge to make sense of their environment. Classrooms can influence development by integrating technology, promoting student-teacher and student-student interaction, and using varied teaching methods.