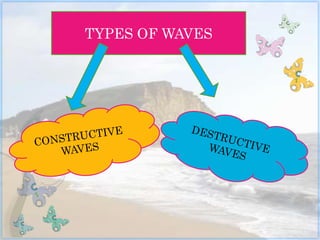
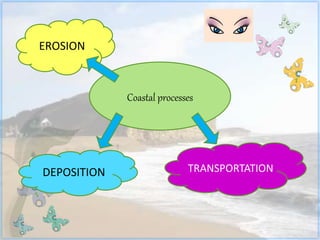
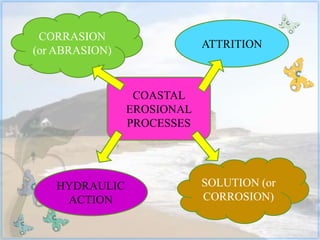
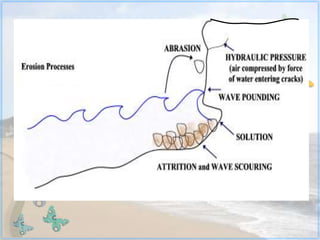
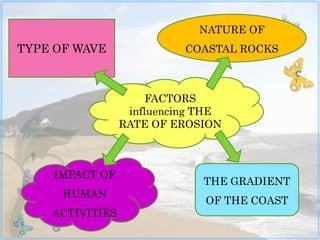
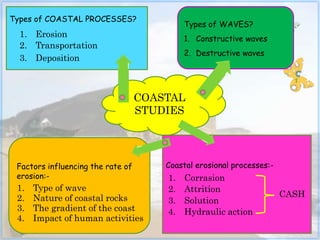
This document discusses coastal studies and processes. It describes the different types of waves that impact coasts, including constructive waves that have weaker backwash and destructive waves that strongly erode coasts. The key coastal processes are erosion, transportation, and deposition. Erosional processes include corrasion, attrition, solution, and hydraulic action, which can be remembered with the acronym CASH. Factors influencing the rate of coastal erosion are the type of waves, the nature of coastal rocks, the gradient of the coast, and human activities.