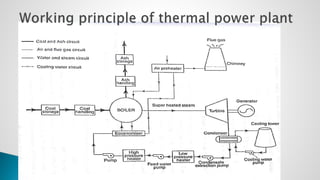
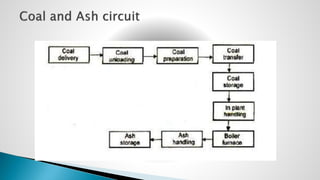
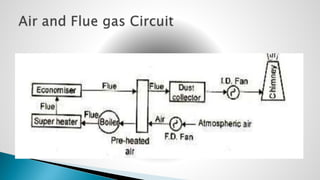
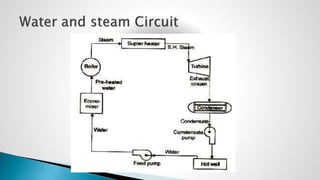
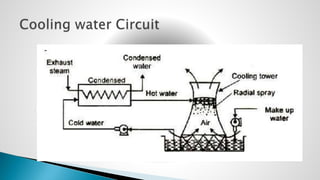
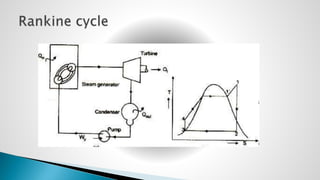
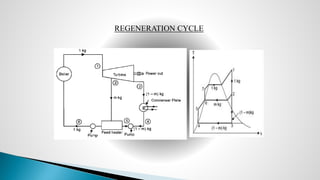
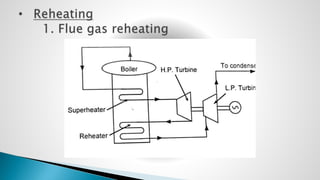
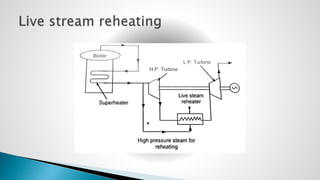
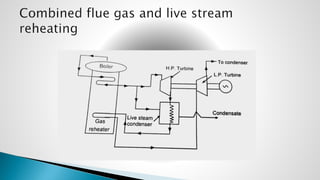
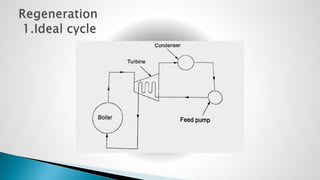
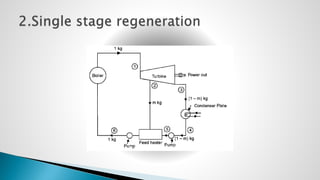
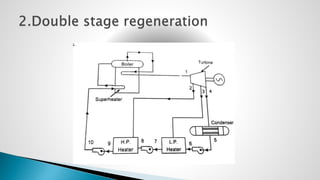
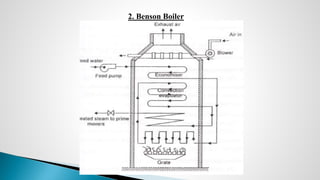
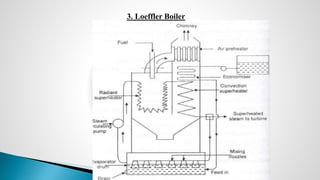
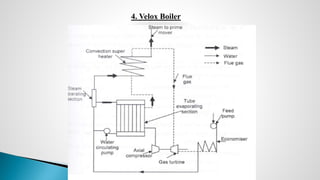
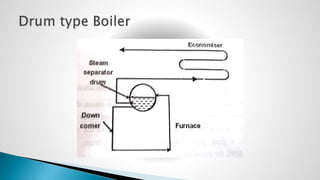
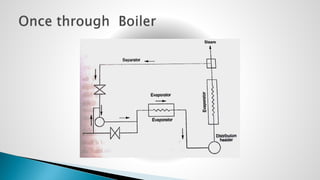
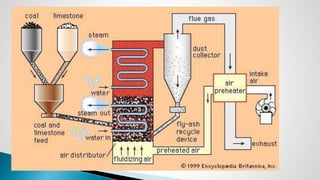
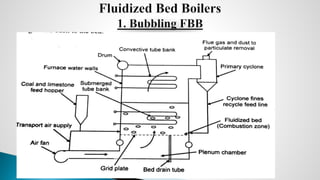
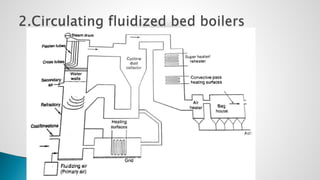
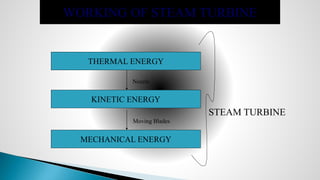
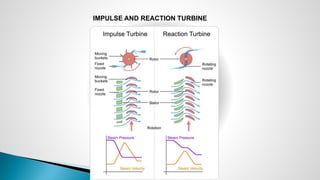
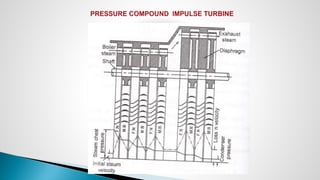
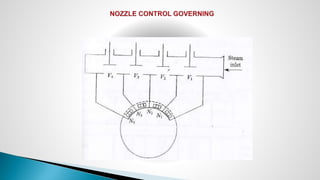
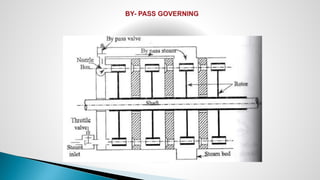
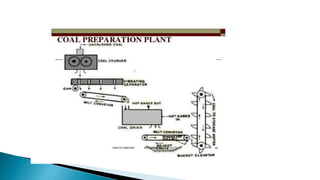
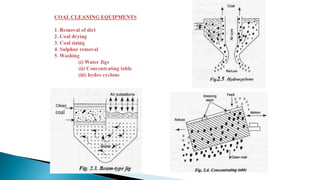
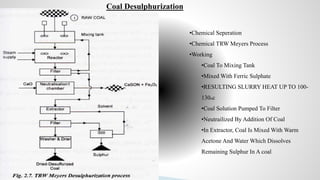
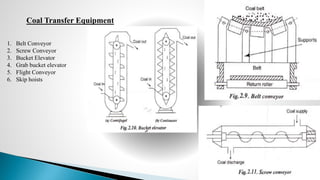
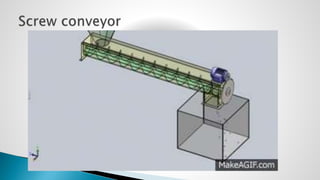
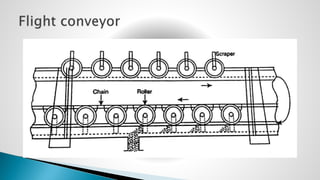
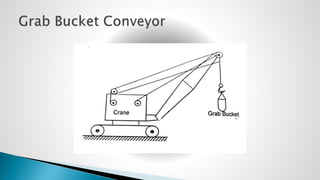
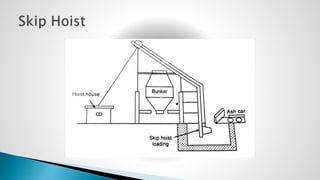
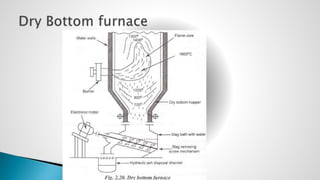
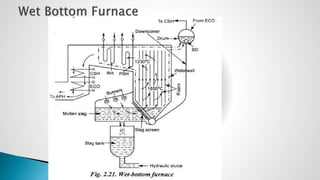
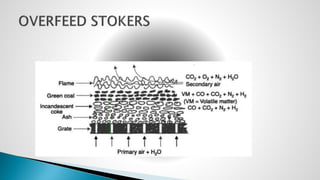
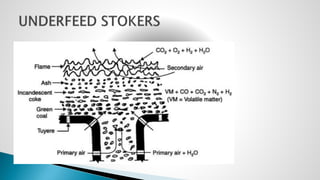
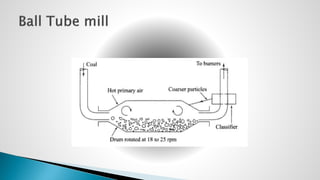
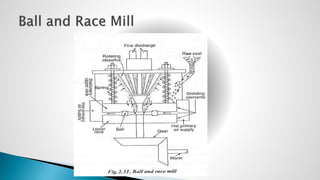
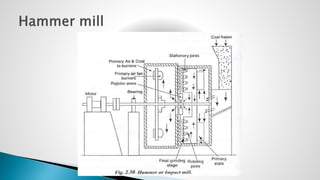
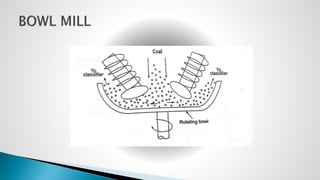
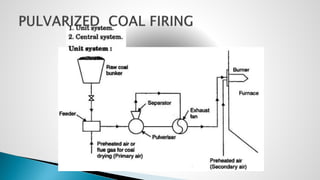
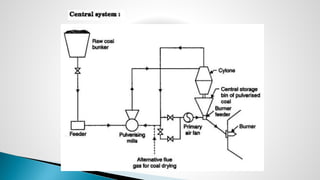
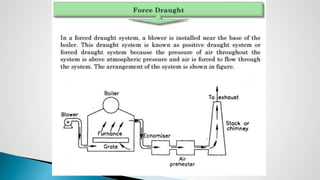
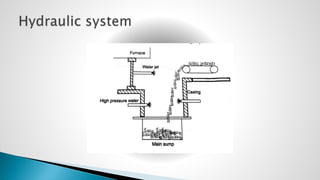
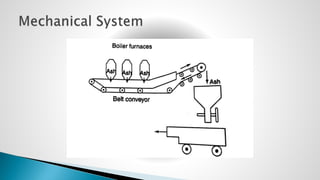
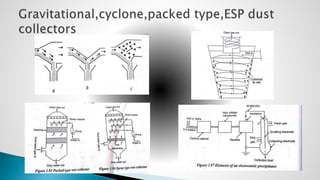
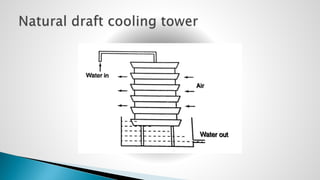
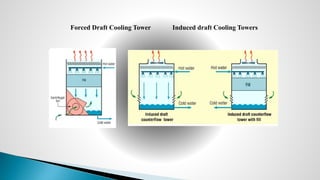
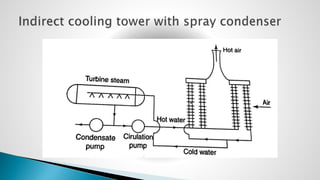
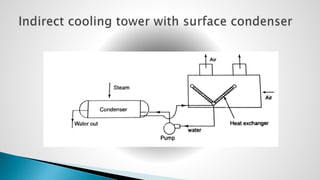
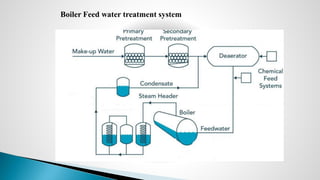
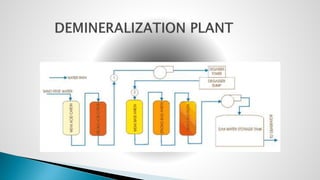
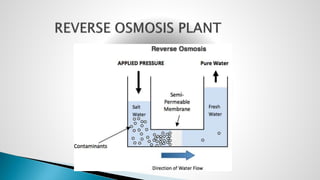
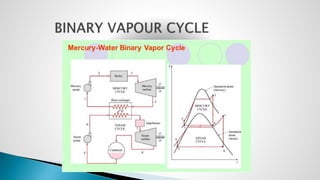
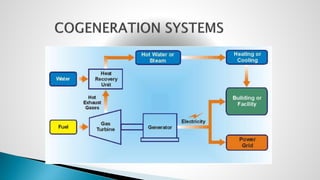
Thermal power plants convert the chemical energy stored in fossil fuels into heat energy by burning coal. The heat boils water to produce steam, which powers turbines that generate electricity. There are four main circuits in a thermal power plant: coal and ash, air and flue gas, water and steam, and cooling water. Coal is burned to heat water and produce steam, which spins turbines to generate electricity. The resulting ash is removed and stored while flue gases are treated before being released into the atmosphere.