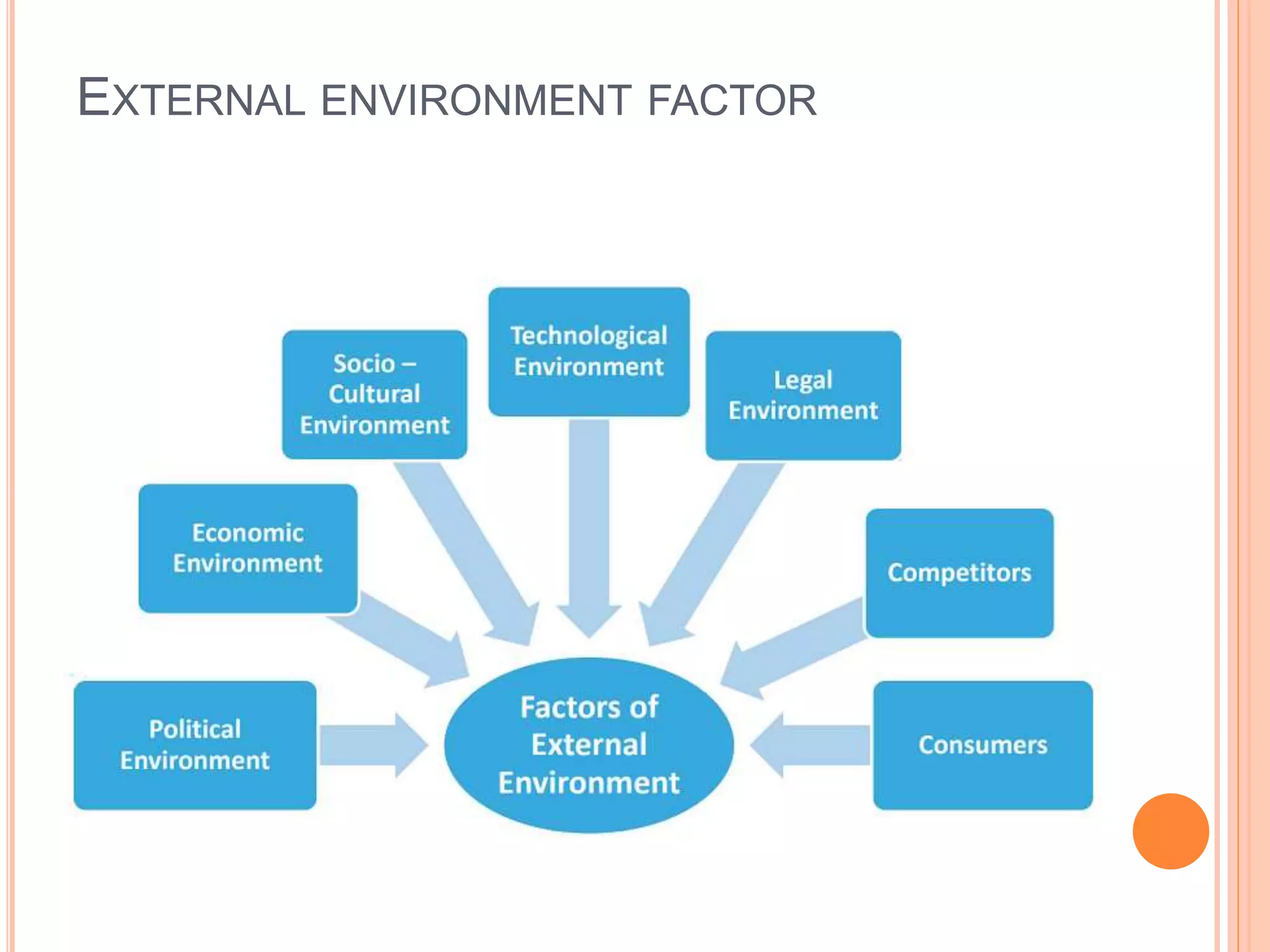
Organizational culture is defined as a system of shared meanings and beliefs within an organization that determine how employees act. It is created through shared values, symbols, rituals, myths and practices. Culture is learned through stories of significant events, rituals, material symbols, and shared language used in an organization. Culture distinguishes one organization from others and facilitates commitment to goals beyond self-interest. Managers are constrained by the actions and activities an organization values and rewards. There are different types of cultures like dominant, weak, and participative cultures. Culture is created by an organization's vision and functions, and managed through selection processes, leadership actions, socialization of new employees, and responsiveness to internal and external environmental factors.