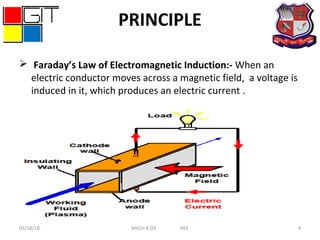
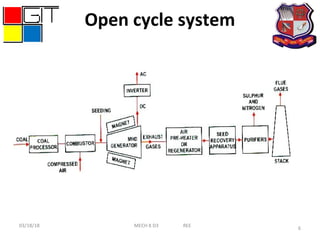
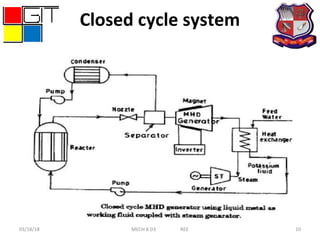
This document presents information about magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) power generation. It discusses the principle of MHD generation using Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. It describes two methods - the open cycle system which directly converts the thermal energy of burned fossil fuels into electricity, and the closed cycle system which uses two working fluids, a liquid metal and inert gas, that are heated and circulated through an MHD generator. Advantages of MHD include high efficiency, lack of moving parts, reliability, and ability to reach full power instantly with low maintenance costs. Disadvantages include short equipment life due to high temperatures and material limitations.