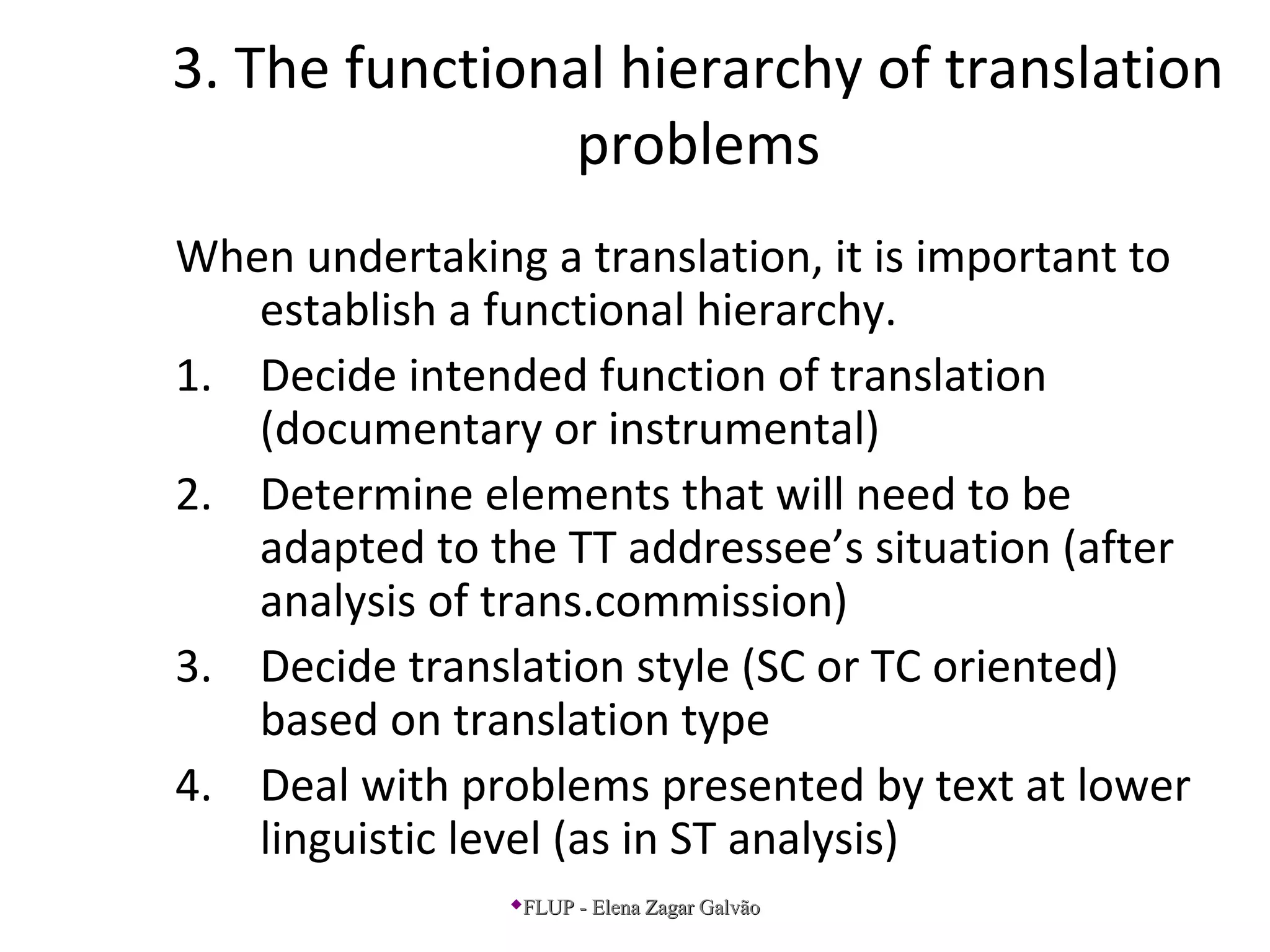
Nord highlights two types of translation: documentary translation, which serves to document a source culture communication, and instrumental translation, which serves as an independent message in the target culture. She also emphasizes three important aspects of translation: 1) considering the translation commission/brief, 2) analyzing aspects of the source text like subject matter and composition, and 3) establishing a functional hierarchy of translation problems from deciding the intended function to addressing lower-level linguistic problems.