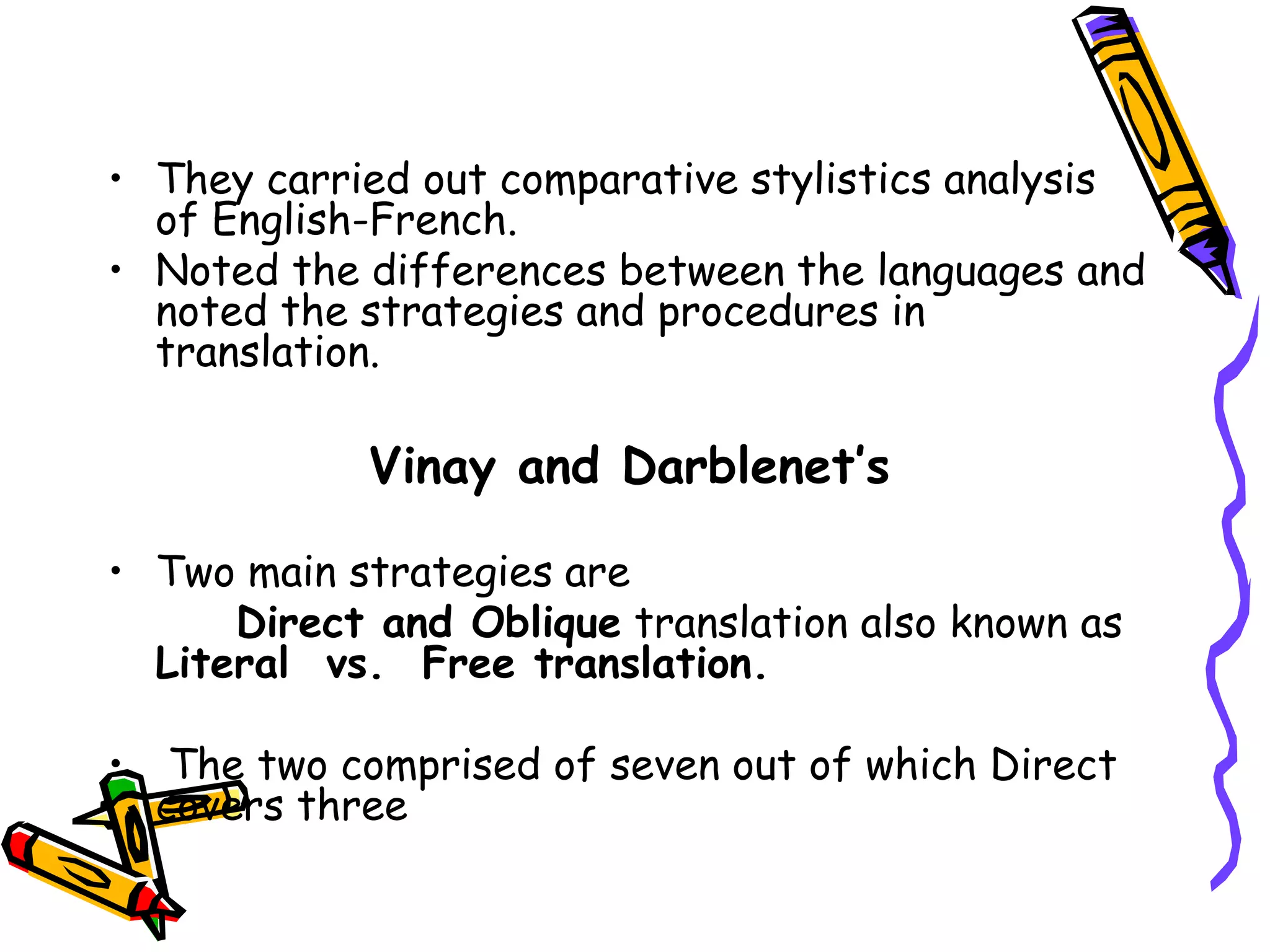
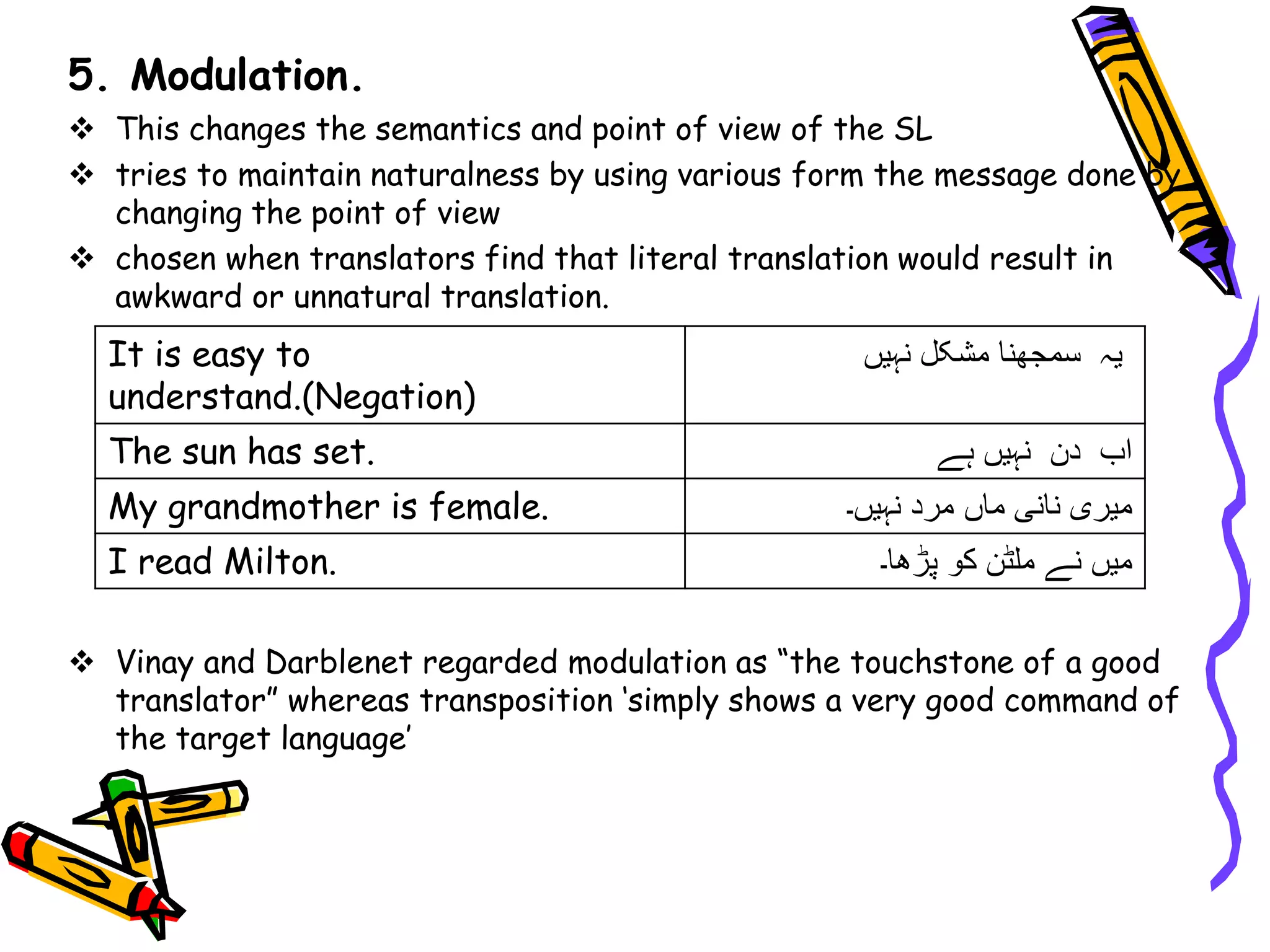
The document discusses Vinay and Darblenet's model of translation, presenting key strategies: direct and oblique translation. It outlines seven specific techniques including borrowing, calque, and literal translation, which emphasize the approach to translating meaning and preserving the structure of the original text. Additionally, it highlights various transformations such as transposition, modulation, and adaptation that aid translators in ensuring naturalness and cultural context in their work.