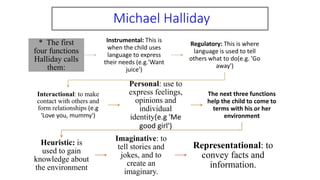
Functional linguistics claims that language use is functional, with the main function being to make meanings. These meanings are influenced by social and cultural context. Language use involves a semiotic process of choosing meanings. Jakobson identifies six communication functions associated with the communication process: referential, aesthetic, emotive, conative, phatic, and metalingual. Halliday sees language as a social/cultural phenomenon. He identifies seven functions language serves for children: instrumental, regulatory, interactional, personal, heuristic, imaginative, and representational. Systemic functional linguistics analyzes language in terms of context, semantics, lexico-grammar, and phonology-graphology. It sees three types of meanings encoded simultaneously