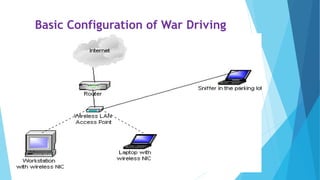
This document discusses wireless LAN security. It describes various wireless LAN technologies and standards. It then discusses some common security issues with wireless LANs like war driving, eavesdropping, denial of service attacks, and rogue access points. It provides solutions for each security issue, such as using encryption, VPNs, firewalls, and tools to detect rogue access points.