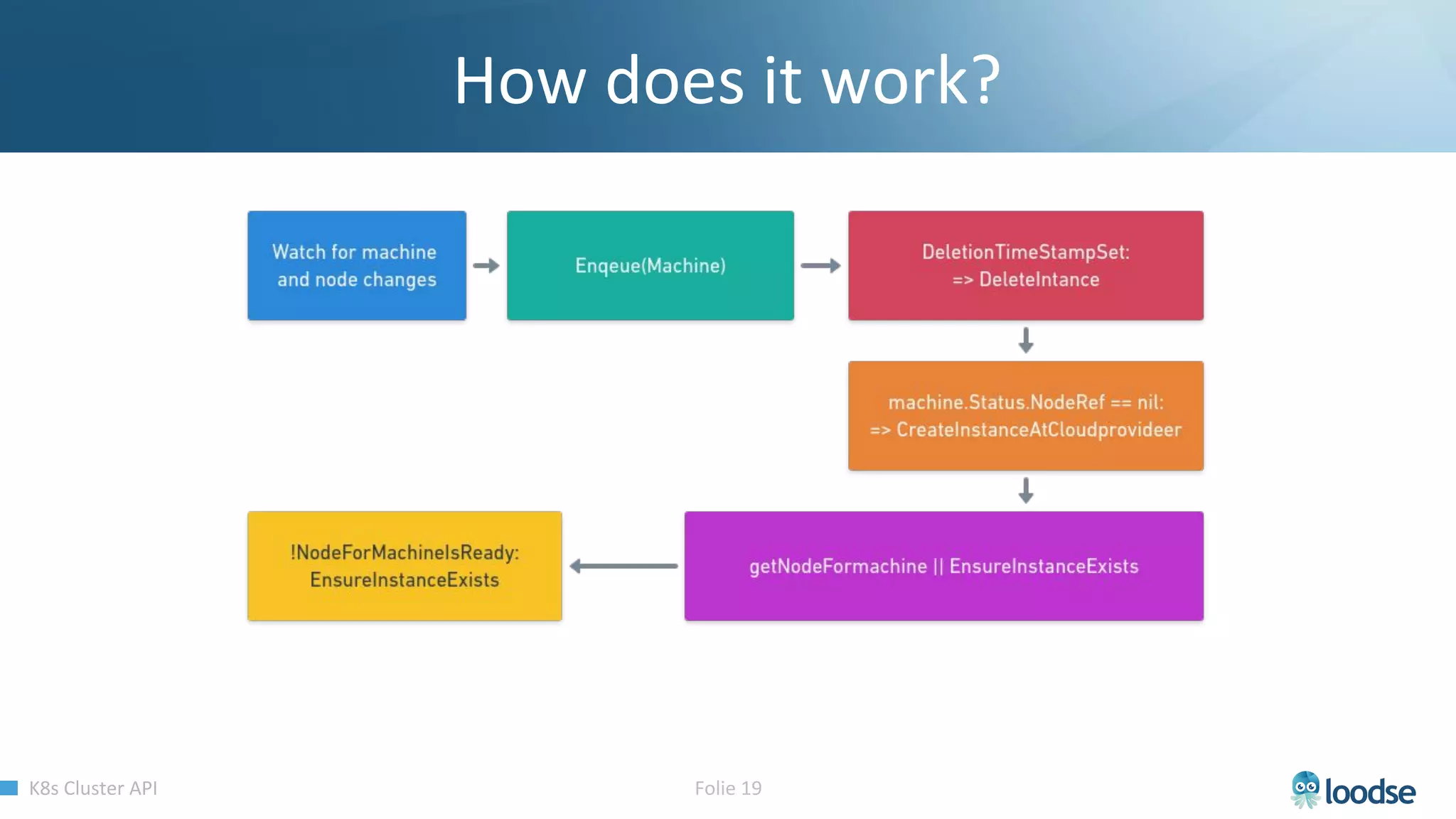
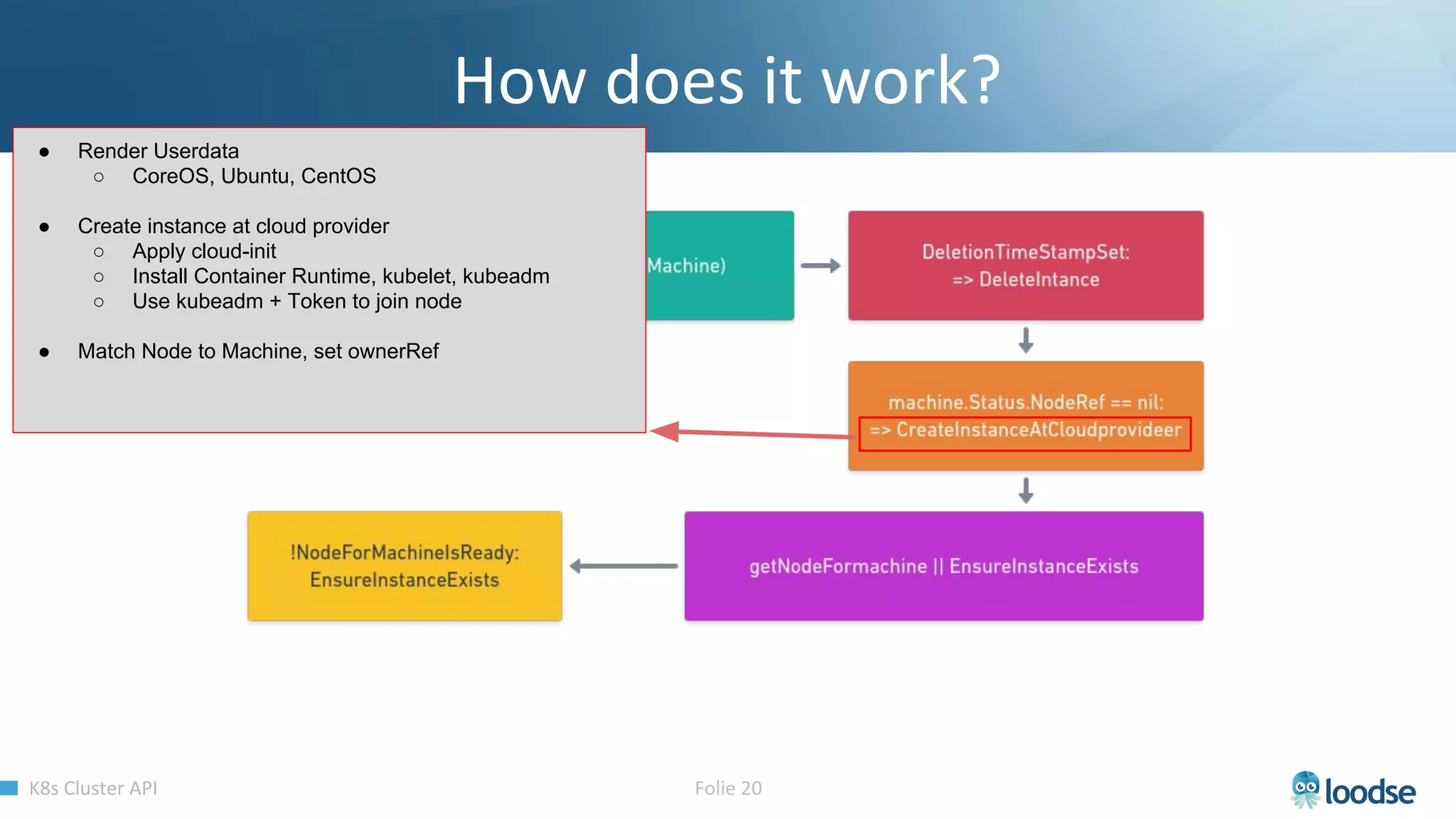
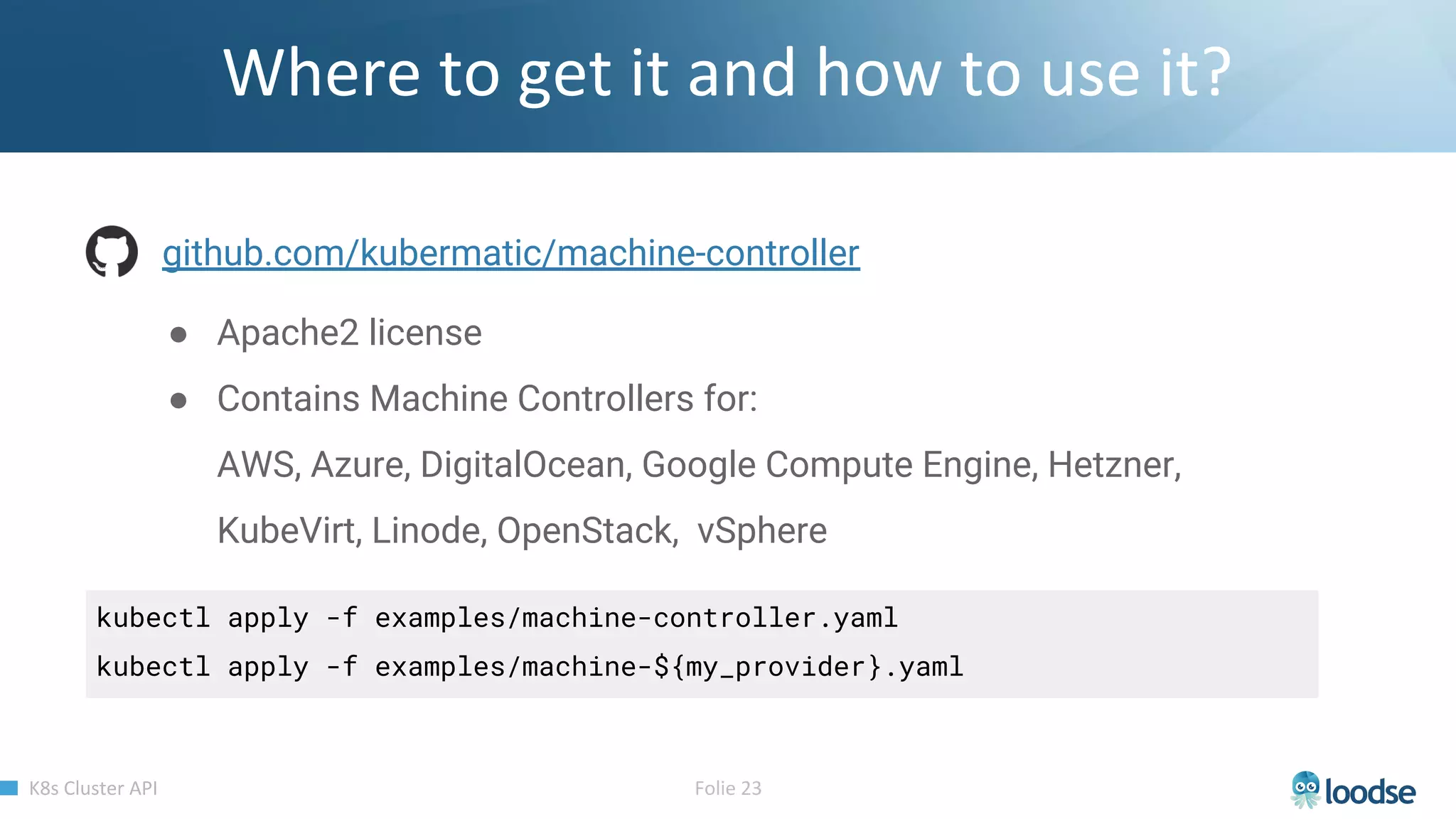
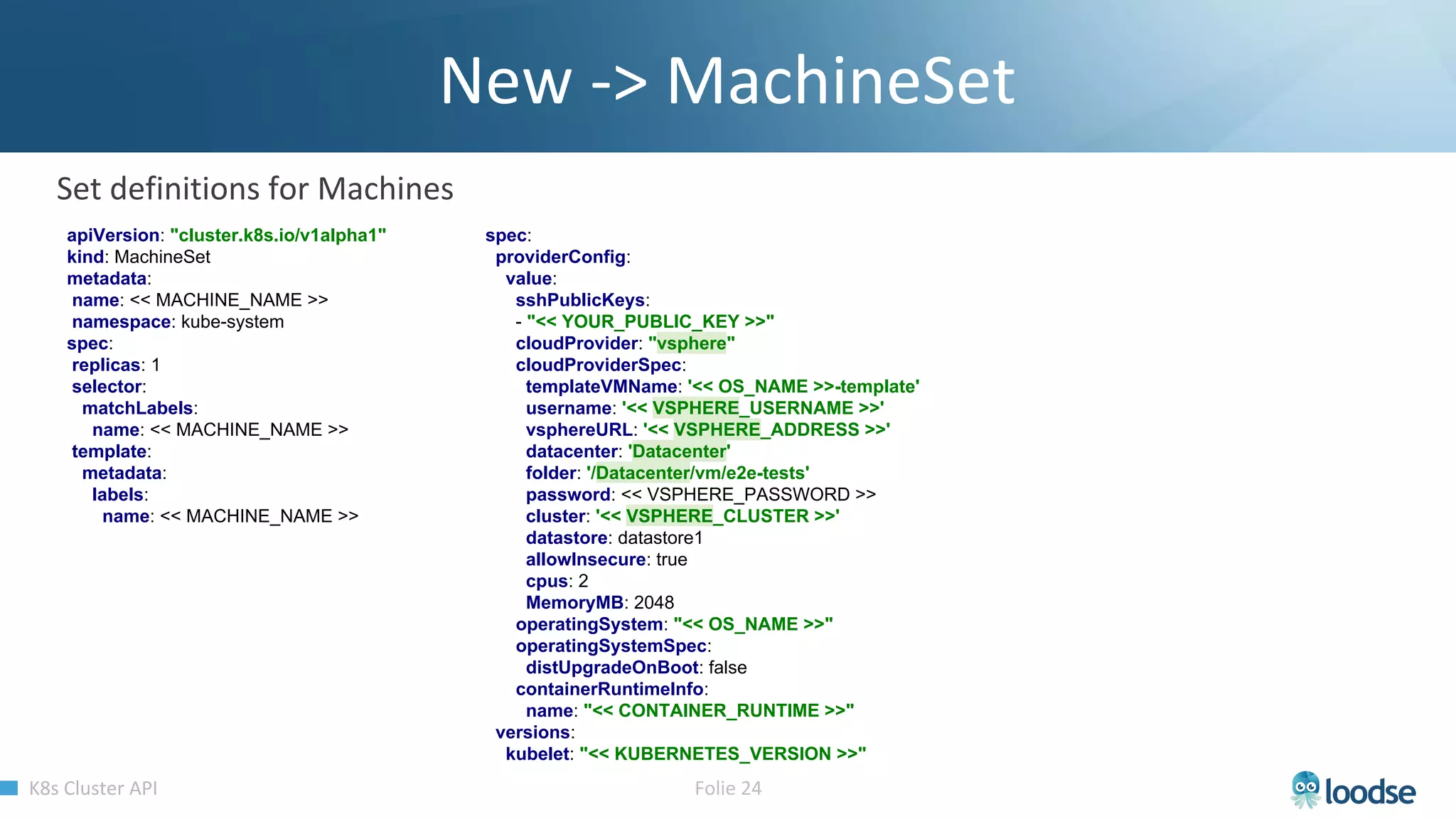
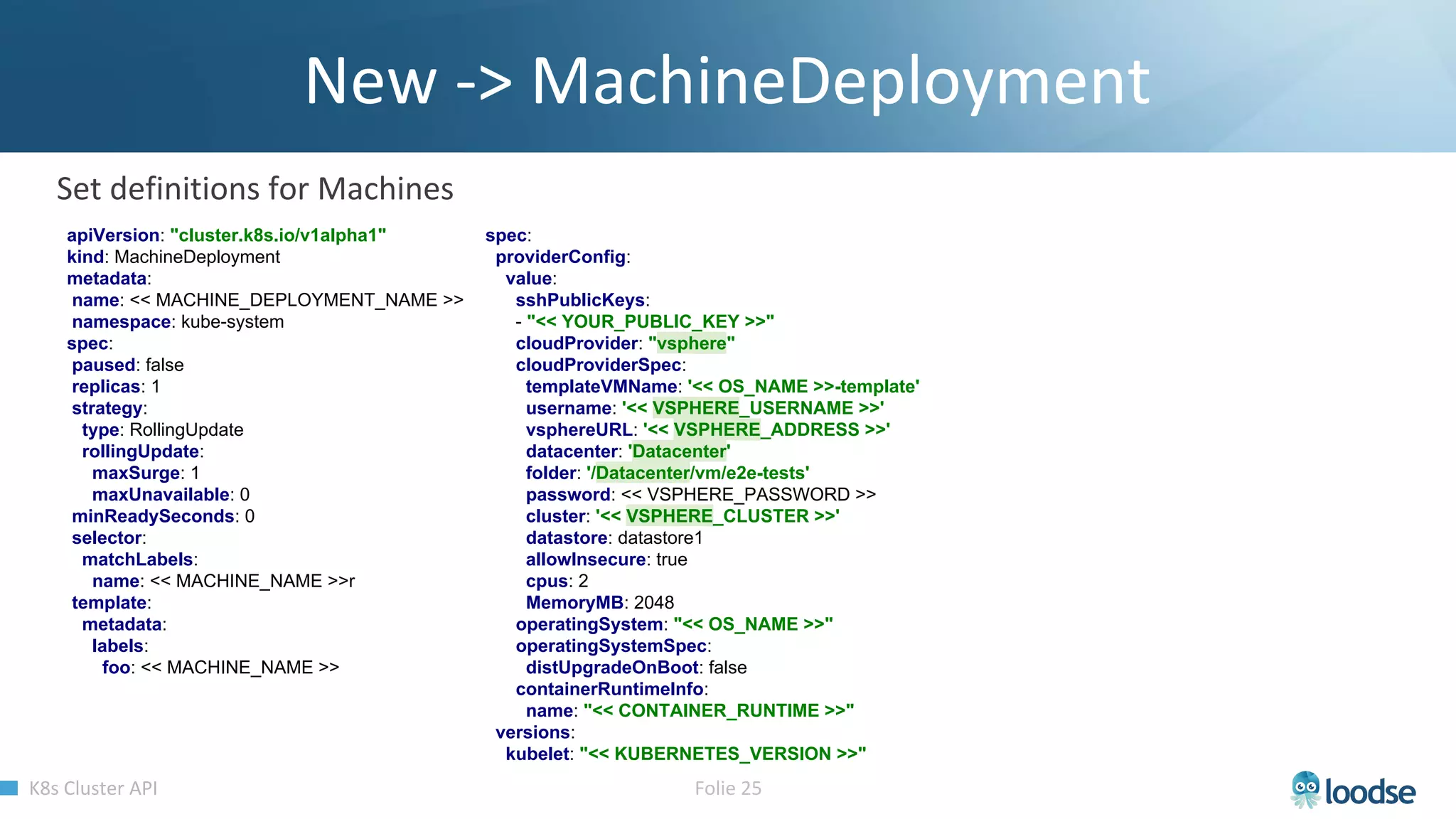
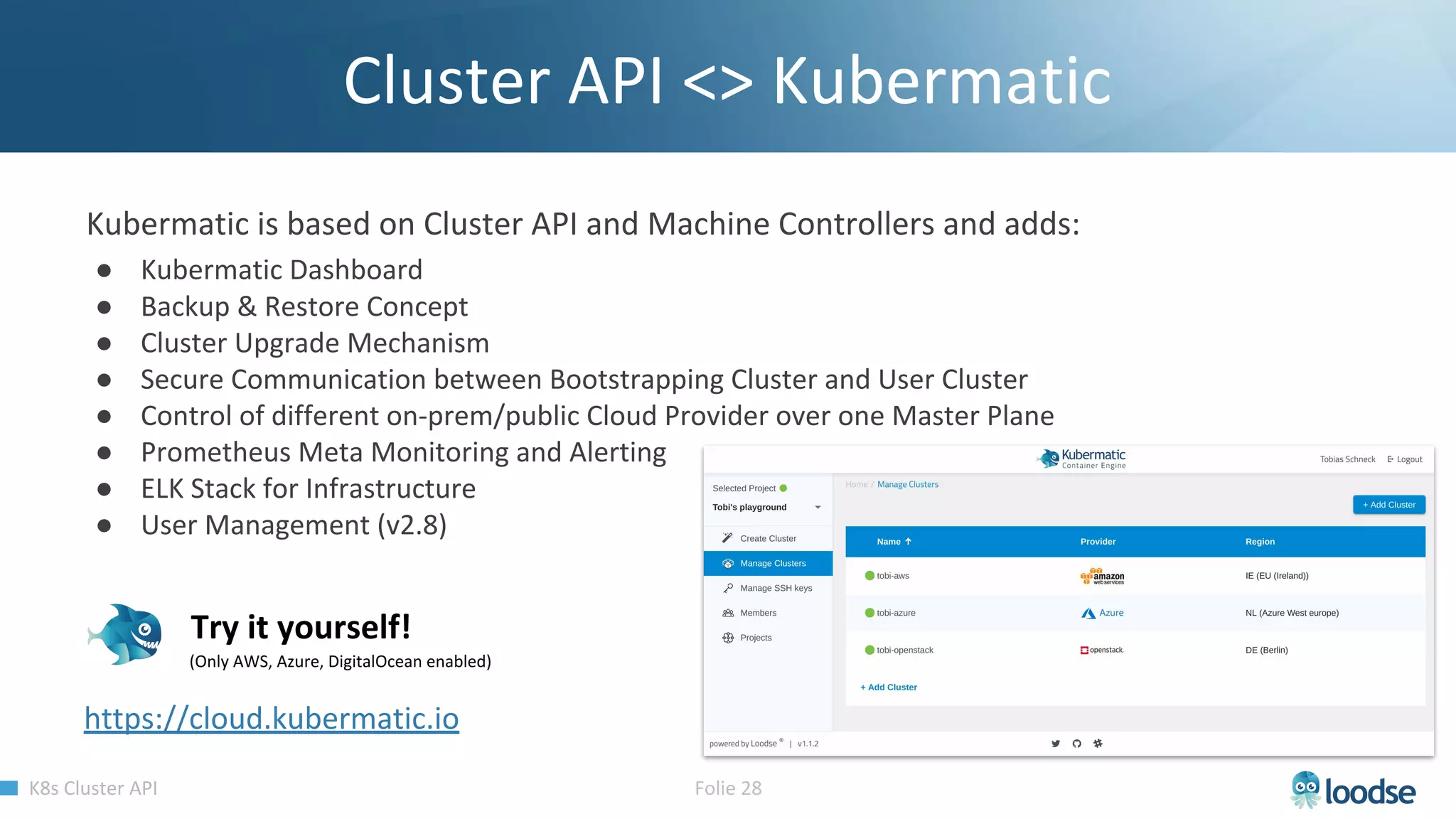
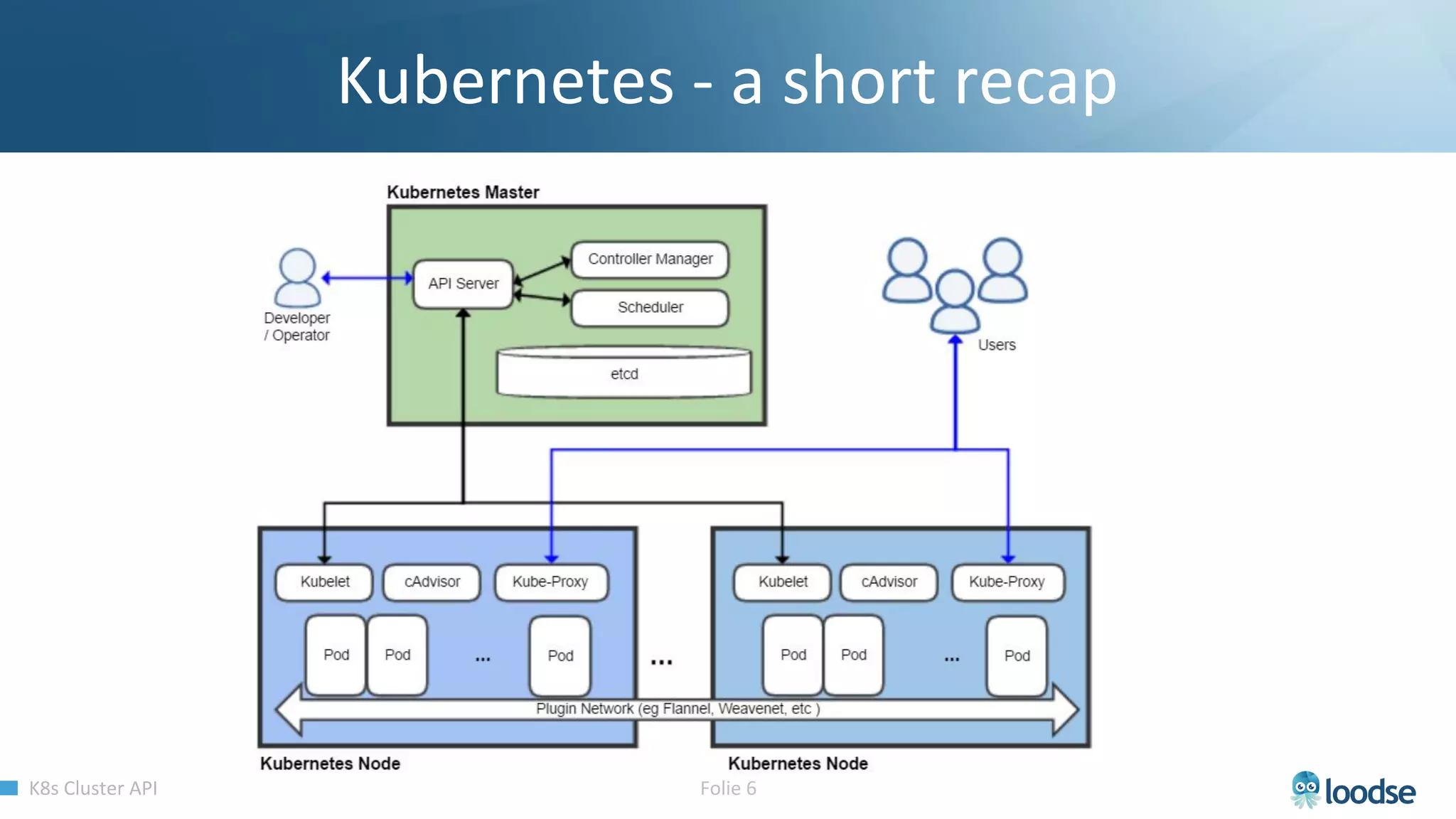
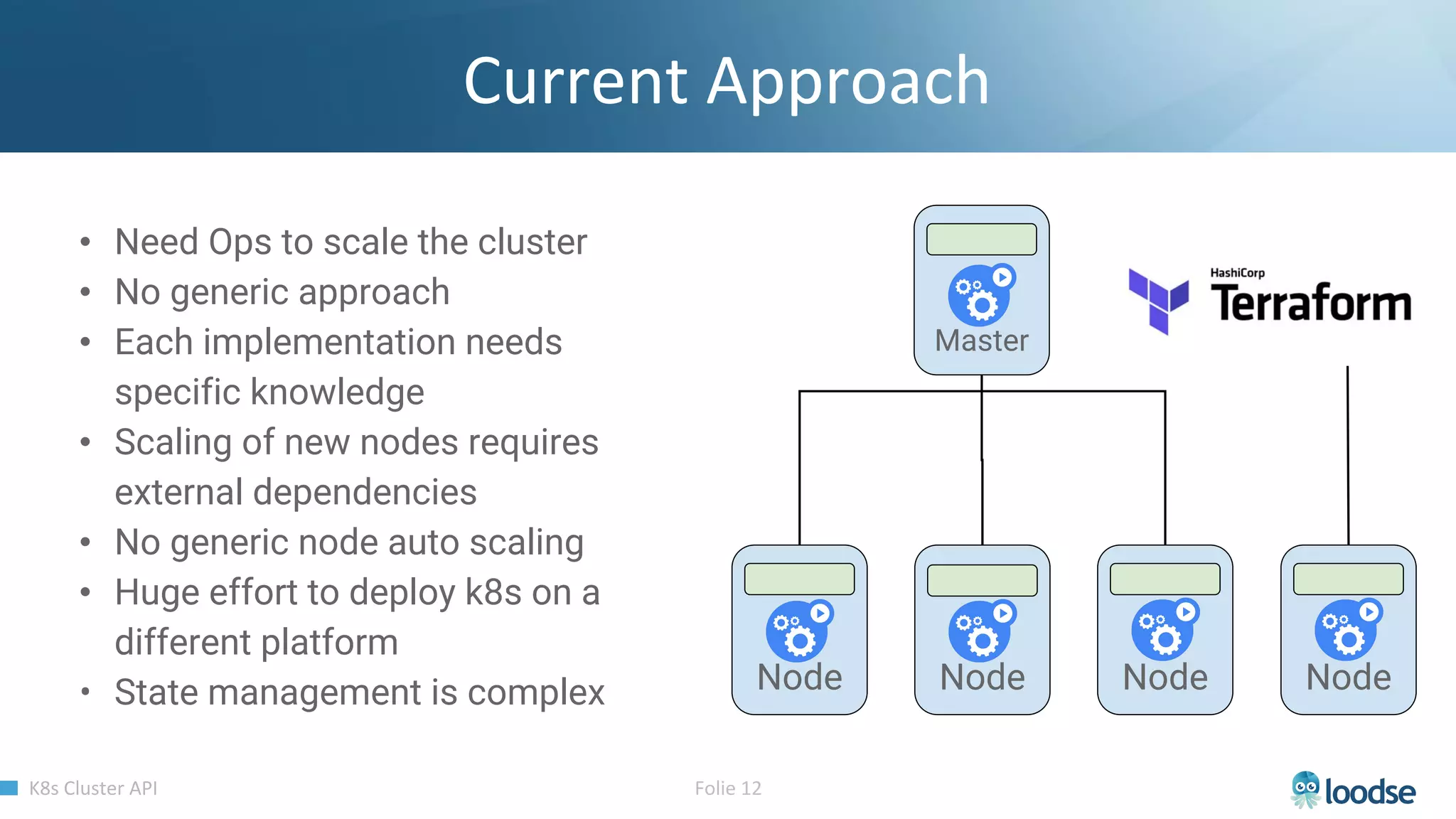
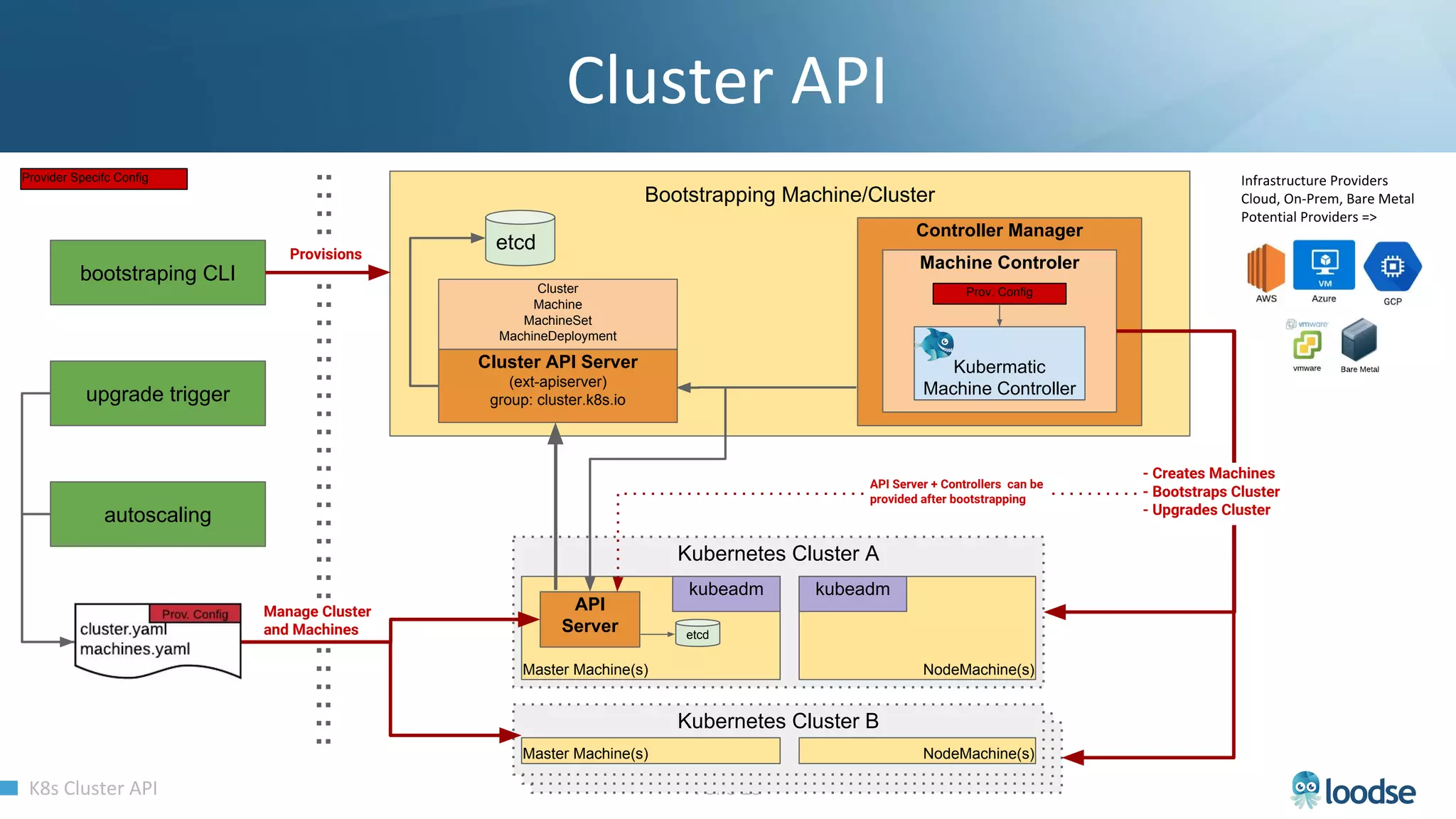
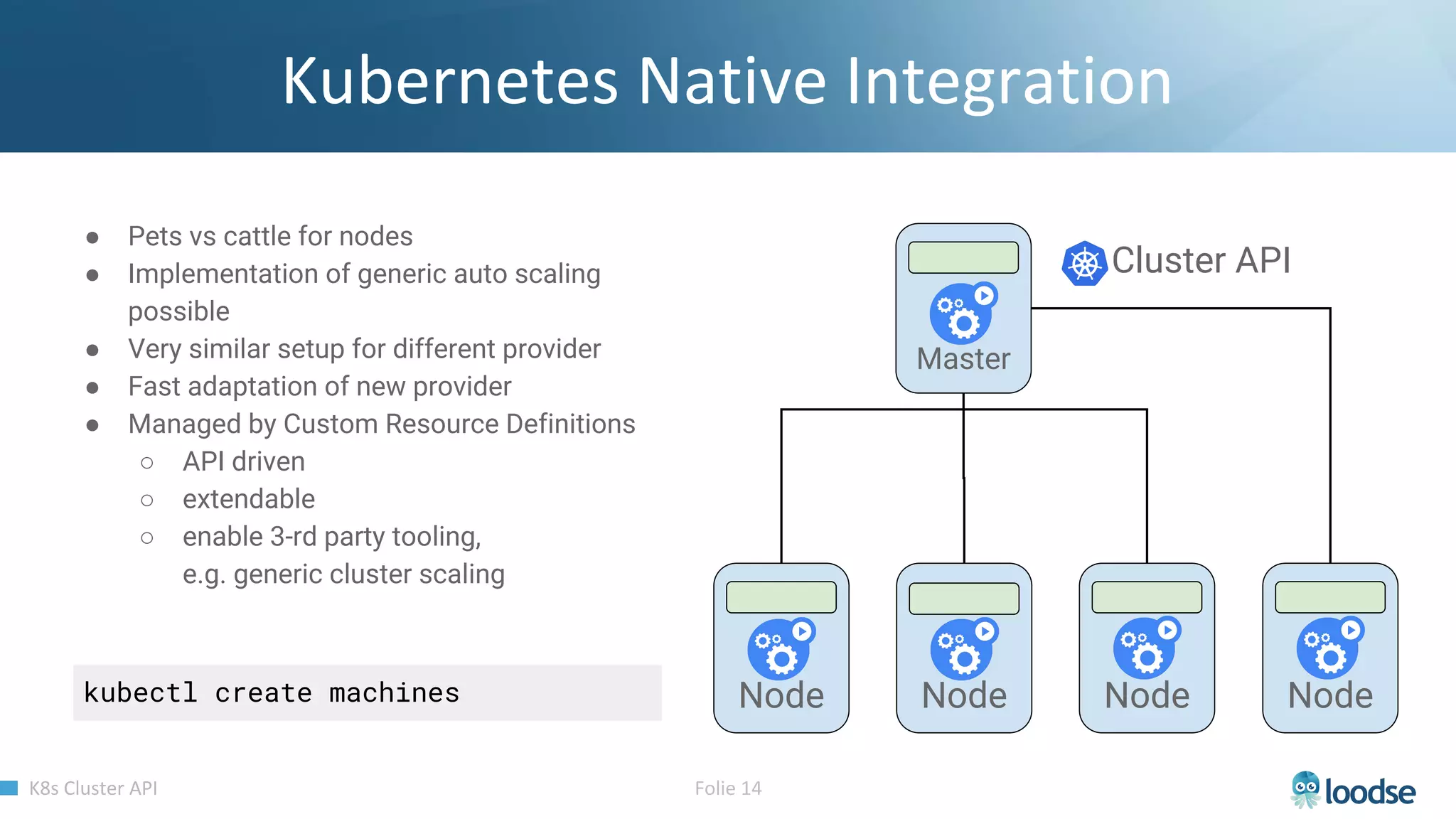
The document promotes a Kubernetes meetup offering a 30% discount on the first ticket and a trial day. It details services provided by Kubermatic, including training, deployment, and management of Kubernetes clusters, along with community contributions like ClusterAPI and machine controllers for various cloud providers. The document also discusses the complexities of scaling and managing clusters in different environments while providing technical specifications and examples for deployment configurations.
















![apiVersion: "machine.k8s.io/v1alpha1"
kind: Machine
metadata:
name: machine1
spec:
metadata:
name: node1
providerConfig:
sshPublicKeys: []
cloudProvider: "hetzner"
cloudProviderSpec:
token: MY-HZ-TOKEN
serverType: "cx11"
datacenter: ""
location: "fsn1"
operatingSystem: "ubuntu"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clusterapi-k8smeetupvienna03-2019-190314093025/75/ClusterAPI-Overview-Managing-multi-cloud-Kubernetes-Clusters-k8s-Meetup-vienna-03-2019-23-2048.jpg)