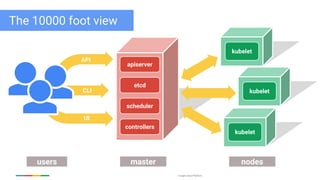
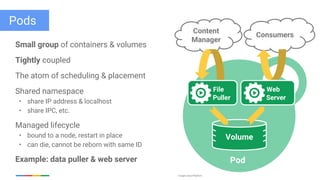
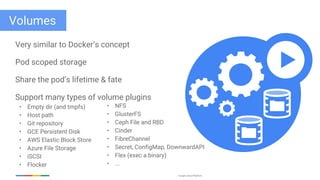
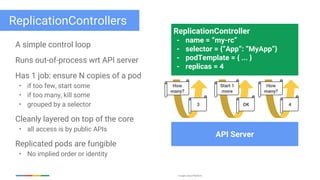
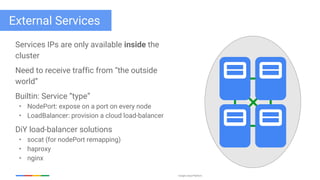
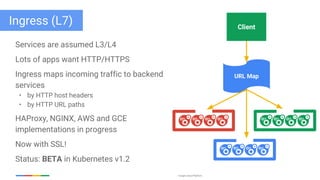
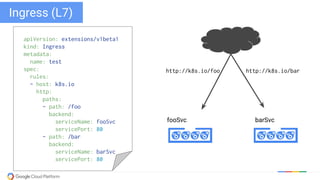
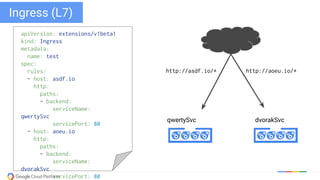
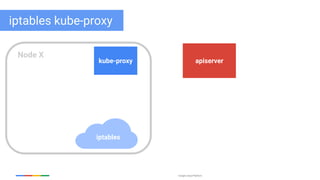
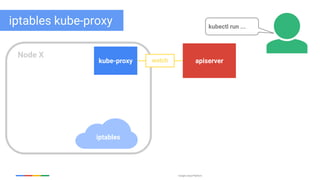
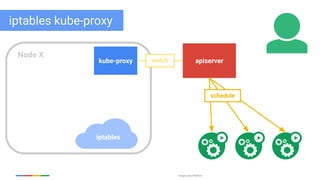
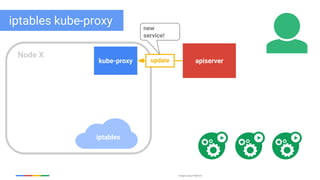
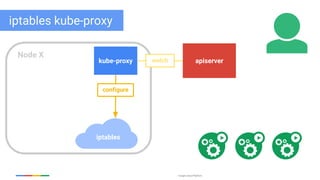
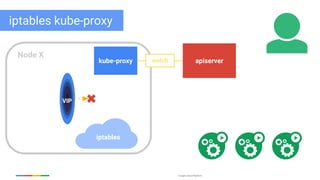
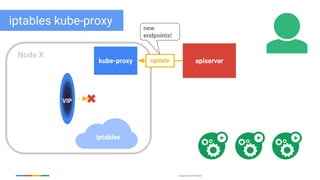
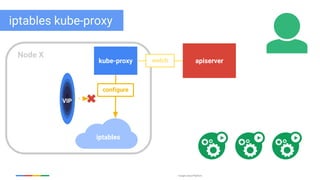
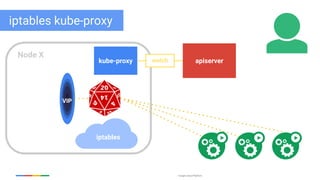
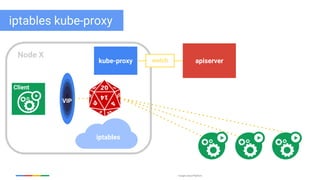
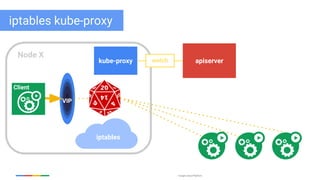
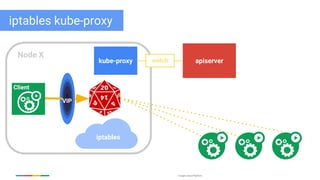
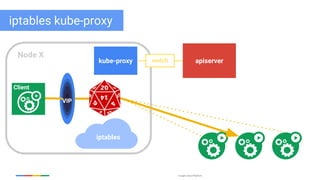
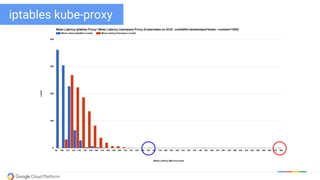
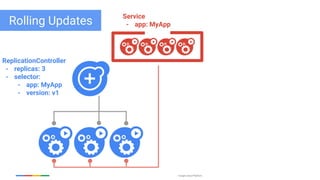
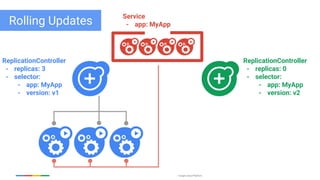
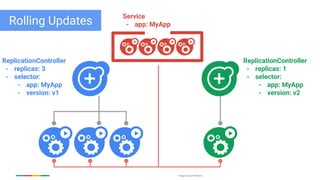
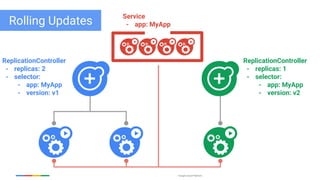
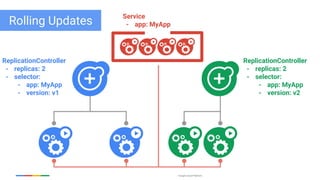
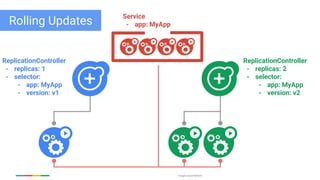
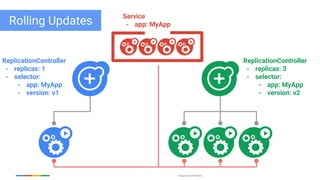
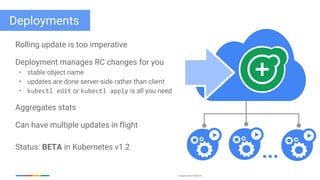
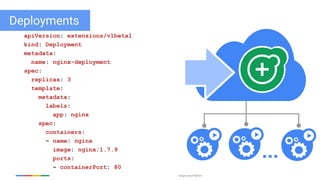
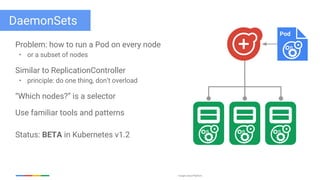
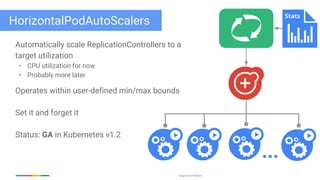
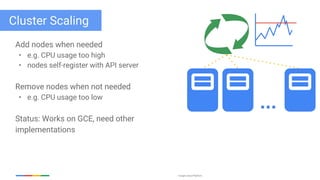
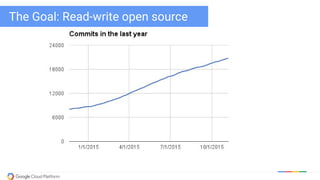
The document discusses updates and features of Kubernetes, highlighting its ability to manage containers across various cloud environments, its open-source nature, and components like pods, services, replication controllers, and more. It covers advancements in ingress handling, rolling updates, jobs, and autoscaling, emphasizing Kubernetes' role in managing application lifecycles efficiently. The presentation also outlines Google's commitment to continuous improvement of the Kubernetes platform and its integration with Google Cloud services.