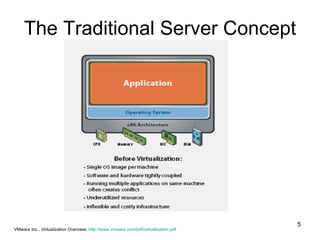
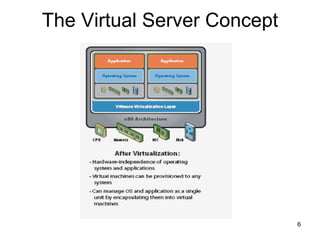
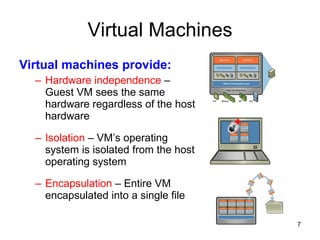
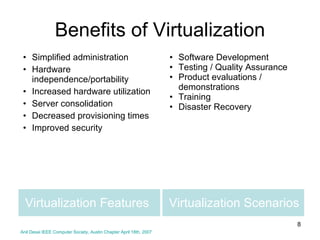
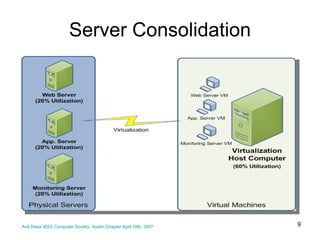
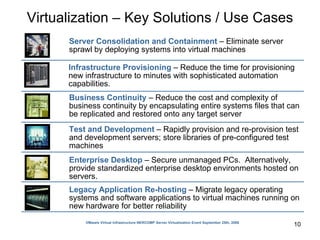
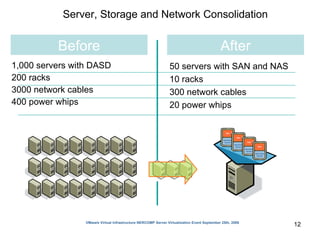
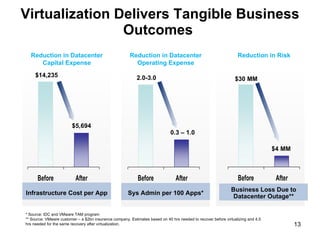
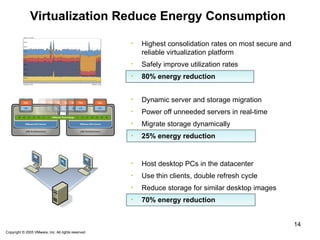
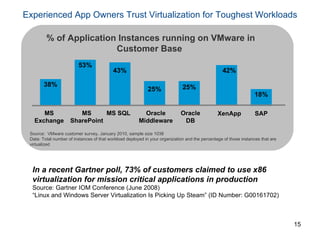
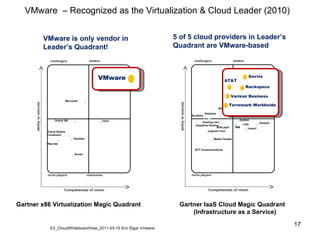
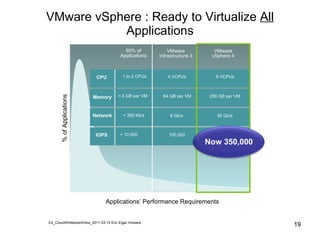
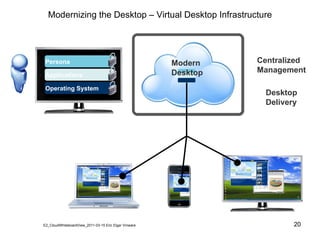
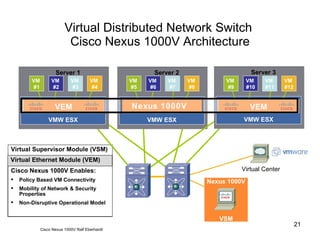
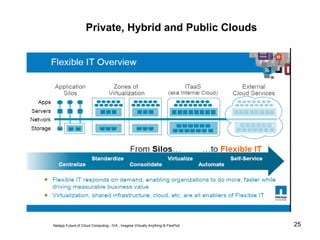
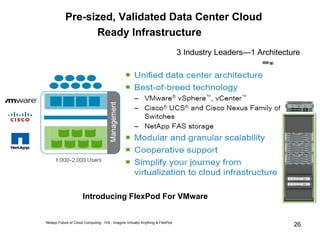
Virtualization abstracts the underlying physical hardware and allows multiple virtual machines to run on the same server. This provides benefits like server consolidation, increased hardware utilization, and improved security. While virtualization works well for most applications, some resource-intensive or real-time applications may have performance limitations in a virtualized environment. Virtualization is now being applied at larger scales through cloud computing, where virtual machines and services can be provisioned on-demand from large-scale data centers.


![Virtualization abstracts the underlying physical structure of various technologies. Virtualization, in computing, is the creation of a virtual (rather than actual) version of something, such as a hardware platform, operating system, a storage device or network resources [1] Server virtualization [2] Creates multiple isolated environments Allows multiple OS’s and workloads to run on the same physical hardware Solves the problem of tight coupling between OS’s and hardware What is Virtualization (1) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtualization (2) Anil Desai IEEE Computer Society, Austin Chapter April 18th, 2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualizationmeisen042811-110502175100-phpapp02/85/Virtualization-meisen-042811-3-320.jpg)