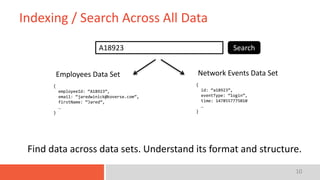
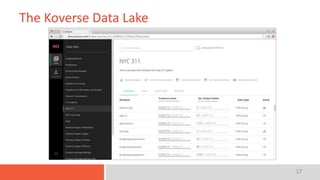
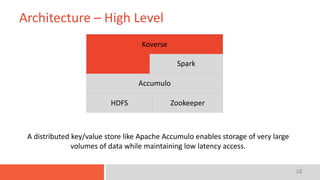
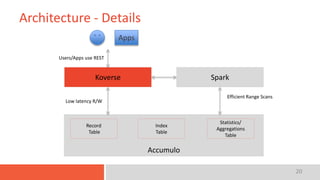
The document discusses the concept of a data lake, emphasizing that it serves as a centralized repository for diverse data within an organization while outlining key characteristics such as indexing, interactive access, multi-level access control, and integration with data science tools. It also highlights the importance of implementing a robust architecture that supports scalability and efficient data access. The presentation's conclusion encompasses a case study of Koverse's data lake architecture.