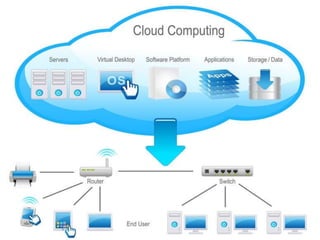
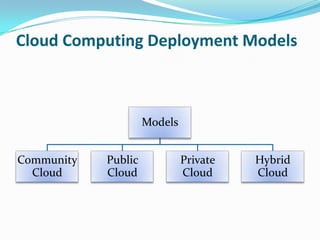
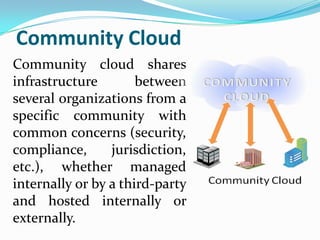
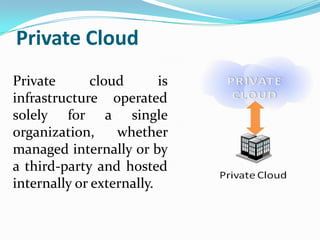
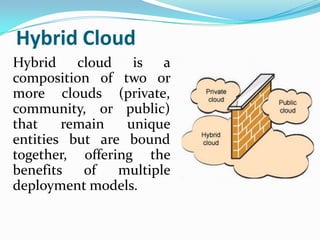
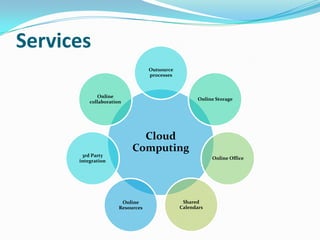
Cloud computing allows users to access applications and files from any device with an internet connection. It provides computation resources, software, data access, and storage through remote servers rather than local hardware. There are different types of cloud deployment models including public, private, hybrid, and community clouds that are distinguished by their intended user base. The cloud architecture consists of a front-end interface and back-end servers that host applications and store data.