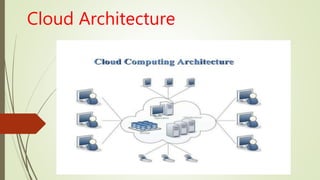
The document provides an overview of cloud computing including:
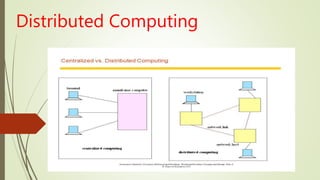
- Definitions of distributed computing, cluster computing, utility computing, and cloud computing as trends in computing.
- A brief history of cloud computing including early concepts in the 1960s and milestones like Salesforce.com in 1999 and Amazon Web Services in 2002.
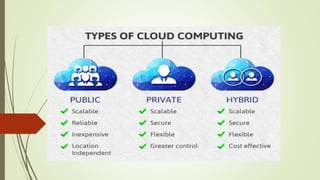
- Descriptions of the types of cloud including public, private, hybrid, and community clouds.
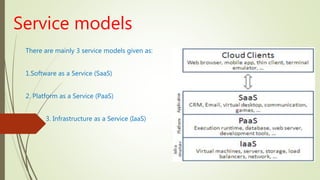
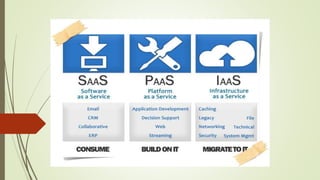
- Explanations of cloud service models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Discussions of cloud storage and advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.
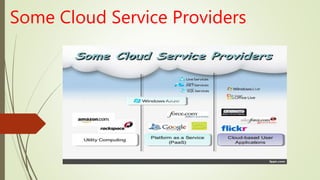
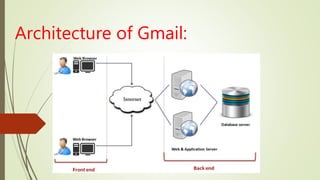
- Real-life examples of