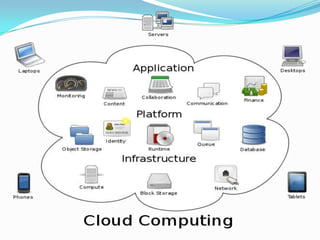
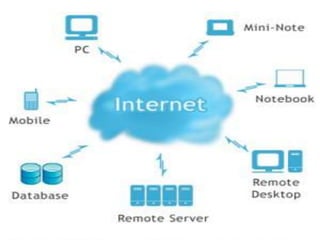
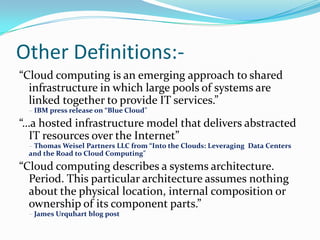
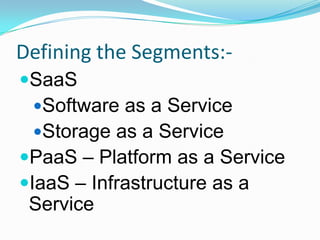
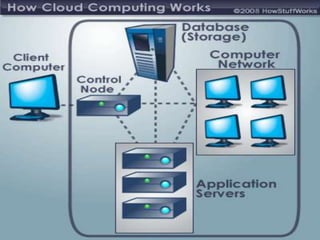
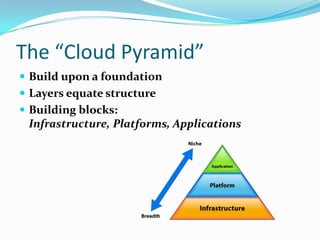
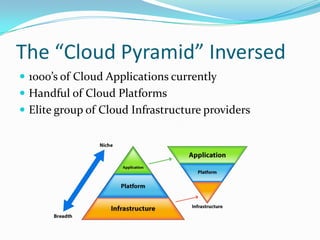
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to shared computing resources and infrastructure over the Internet. It is divided into front-end and back-end components that connect through a network. The front-end includes client interfaces, while the back-end comprises servers, storage, and other resources that create the "cloud". Cloud services are delivered dynamically and billed based on usage. Resources are shared in a multi-tenant model accessible from any device.