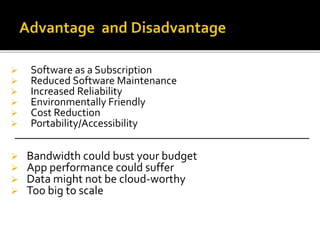
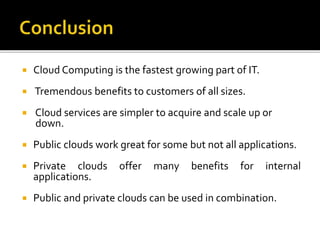
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including definitions of cloud computing, its history and characteristics. It discusses the types of cloud deployment models (public, private, hybrid etc.), types of cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), common cloud applications, advantages and disadvantages. The document aims to explain what cloud computing is, how it works, why it is useful and some considerations around using cloud services.