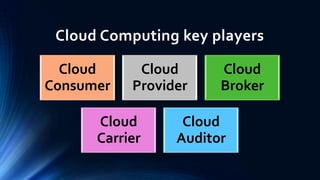
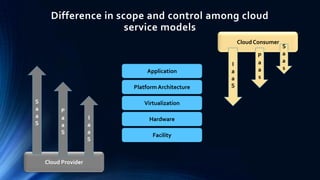
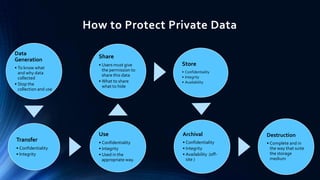
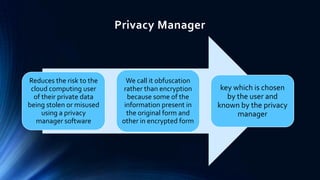
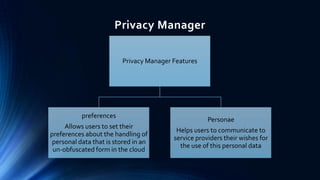
This document discusses privacy protection issues in cloud computing. It begins by defining cloud computing and privacy protection. The main privacy issues in cloud computing are lack of physical control over data, difficulty tracking and protecting all copies of data, and legal problems due to varying privacy laws across regions. The document proposes using a privacy manager software to help users obfuscate sensitive metadata attributes before sharing data in the cloud. This allows users to set preferences and personae to control how their personal data is handled and used by cloud services.