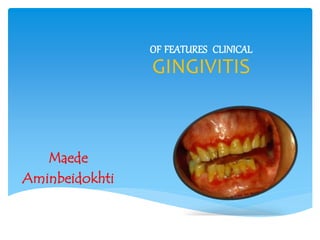
Clinical features of gingivitis
- 2. Classification Of Gingivitis Course and duration Acute gingivitis - can occur with sudden onset and short duration. Recurrent gingivitis – reappears after treatment Chronic gingivitis – slow in onset and of long duration Distribution Localised – confined to single tooth or a group Generalized – involves entire mouth • • • Marginal – involves gingival margin Papillary – involves interdental papilla and extends into gingival margin. Earliest signs of gingivitis occur in the papillae. Diffuse – affects marginal, attached gingiva and interdental papillae.
- 7. CliniCal findings • • Systematic approach is required. An orderly examination of gingiva BlEEding On PROBing 2 earliest signs of gingival inflammation preceding established gingivitis. • • Gcf production increased Bleeding on probing ( easily detectable (
- 8. • • Easily detected clinically and therefore is of value for early diagnosis and prevention of advanced gingivitis Bleeding appears earlier than other visual signs of inflammation. • It is a more objective sign that requires less subjective estimation by the examiner • Interestingly numerous studies show that smoking suppresses the gingival inflammatoryresponse.
- 9. ACUTE BLEEDING … -Injury or acute gingival disease Laceration of the gingiva - biting on sharp pieces of food. - toothbrush trauma - toothpicks - burns from hot foods or chemicals • Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis blood vessels exposed to the surface by necrosed epithelium so spontaneous bleeding or bleeding on slight provocation occurs.
- 10. Bleeding associated with systemic changes Spontaneous or after irritation… -varied etiology and manifestations… -underlying cause “haemostatic system failure” bleeding in the skin , internal organs other Tissues…. vascular abnormalities platelet disorders hypoprothrombinemia coagulation defects multiple myeloma other causes …
- 13. Gingival bleeding on probing
- 14. color chanGes coral pink effected by • • Normally… vascularity Keratinisation --- Red or pale pink Chronic increased vascularity. reduced keratinisation. venous stasis --- bluish hue Acute Colour changes differ in nature and distribution • • • Marginal (acute necrotising ulcerative ging) Diffuse (herpetic gingivostomatitis) Patchlike (chemical reactions )
- 17. metallic piGmentation Heavy metals absorbed systemically… occupational therapeutic household …discolor the gingiva. bismuth lead Hg Ag
- 18. Pigmentation can be seen as • Black or bluish line ( gingival contour ( • Isolated blotches (interdentally marginal or attached gingiva ( Metal pigments … Systemically absorbed. Perivascular accumulation Vessel rupture ( inflammatory) Increased vascular permeability Seepage of metal into surrounding tissue ( sub epithelial c.t.) …NOT DUE TO TOXICITY…
- 21. Bismuth gingivitis. linear black discoloration of the gingiva in a patient receiving bismuth therapy. Discoloration of the gingiva caused by embedded metal particles (amalgam(
- 22. Treatment…? simply TREAT the Inflammation… CoLor Changes – systemiC faCtors - Non specific - Further diagnostic efforts - Referral to specialist Endogenous pigmentations MELANIN BILIRUBIN IRON
- 23. Melanin Physiologic pigmentation. Pathologies… Addison’s disease Peutz-Jegher’s disease Albright’s syndrome Bile pigment. Yellowish color oral mucosa ( apart from sclera) Other causes.. Diabetes Pregnancy Blood dyscrasias Anemia Polycythemia etc
- 24. exogenous • • • • Metal dust… coal. Coloring agents. In foods , lozenges Tobacco --- hyperkeratosis, increase in melanin pigmentation Amalgam implantation – localised bluish black areas Discoloration of the gingiva caused by embedded metal particles (amalgam(
- 25. ConsistenCy Normally.. Firm and Resilient. • In chronic gingivitis the consistency of the gingiva is determined by the relative predominance of the following changes -Oedematous -Fibrotic )destructive) (reparative( - Combination of either
- 26. CaLCified masses… - isolated - groups traumatically lodged.. substances derived from the tooth. root remnants, calculus cementum fragments cementicles. Associated with… chronic inflammation fibrosis foreign body reaction )origin notcrystalline substances in the gingiva seen at times known(…
- 27. surfaCe texture Loss of stippling ( early sign ( in chronic inflammation… 1)Smooth , shiny 2)Firm and nodular ( also found in drug induced gingival enlargement) - “peeling off” of the surface occurs in the desquamative gingivitis. - leathery texture … hyperkeratosis.
- 28. Position of the gingiva. Recession -actual position -apparent position. Actual : position of the epithelial attachment. Apparent : level of the crest of the gingival margin. 2 types of recession … clinically visible. can only be estimated by insertion of a -visible -hidden probe.
- 30. recession refers to position of the gingiva - NOT the condition of the gingiva. May be - localised. - generalised
- 31. ETIOLOGY OF RECESSION. Age: physiologic process…? (8% incidence in children. 100% in persons aged 50 and above) No convincing evidence… - gradual apical shift : cumulative effect of minor pathologic involvement and repeated direct trauma. Factors responsible…. ( gingival ablation) -Faulty tooth brushing -Tooth malposition -Friction from soft tissues -Gingival inflammation -Frenal pull.
- 32. Changes in Gingival Contour The term Stillman’s clefts has been used to describe a specific type of gingival recession that consists of a narrow, triangular-shaped gingival recession. As the recession progresses apically, the cleft becomes broader, thereby exposing the cementum of the root surface.
- 33. The term McCall festoons has been used to describe a rolled, thickened band of gingiva that is usually seen adjacent to the cuspids when recession approaches the mucogingival junction.
