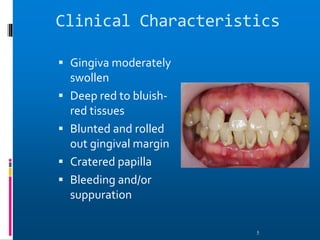
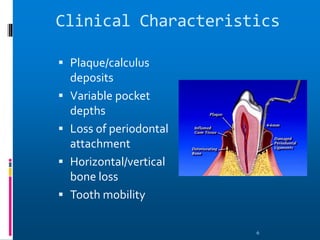
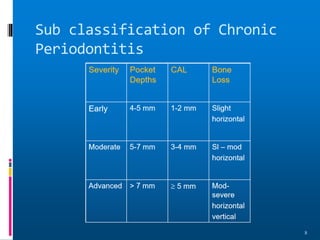
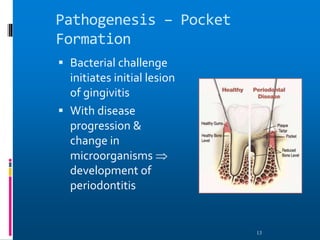
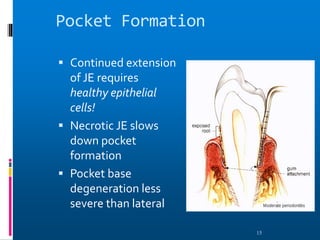
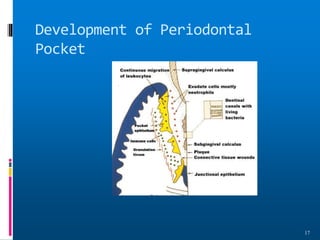
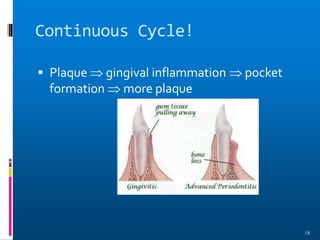
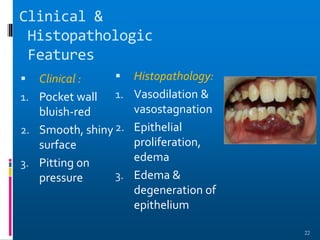
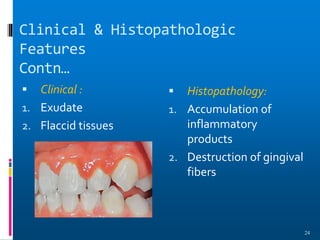
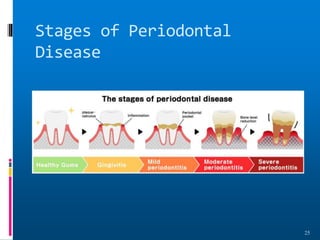
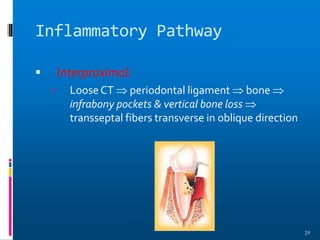
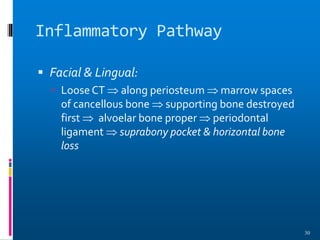
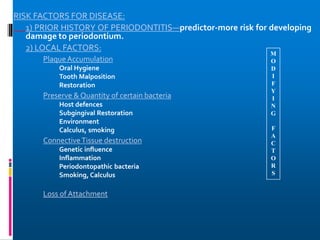
Chronic periodontitis is a slowly progressive infectious disease that results in inflammation of the supporting tissues of the teeth and bone loss. It is caused by an extension of gingival inflammation into deeper periodontal tissues due to plaque accumulation. Key characteristics include a localized or generalized onset at any age, usually in adults, with periods of rapid progression possible. Treatment involves non-surgical procedures like scaling, root planing, and curettage as well as surgical procedures like pocket reduction surgery to correct anatomical defects. Prognosis depends on factors like patient compliance, systemic involvement, disease severity, and status of remaining teeth.