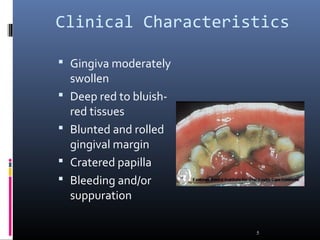
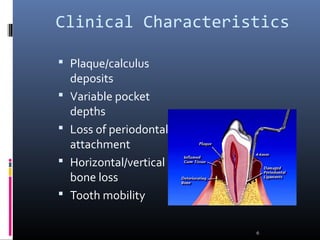
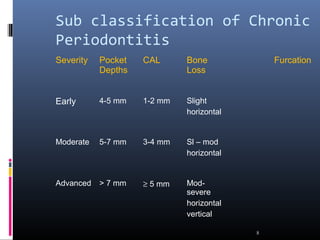
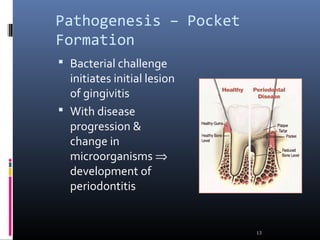
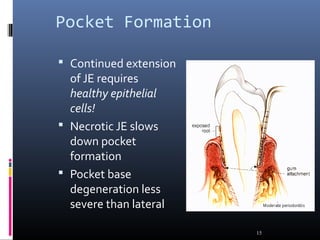
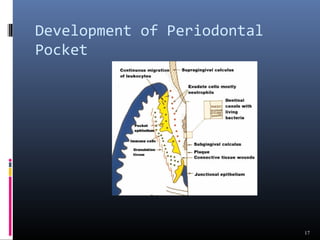
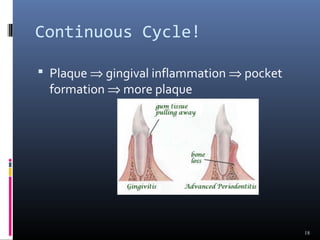
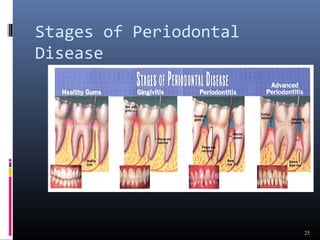
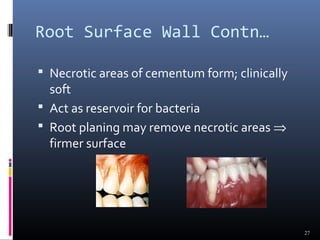
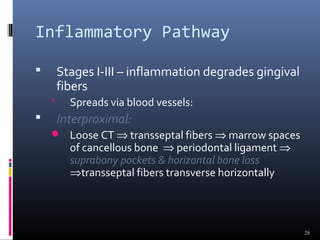
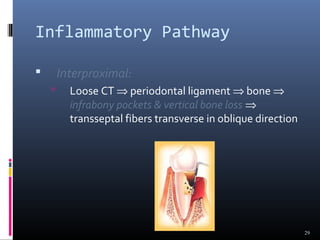
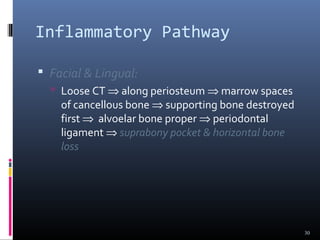
Chronic periodontitis is characterized by inflammation within the supporting tissues of the teeth and progressive bone and attachment loss. It is caused by an extension of gingival inflammation into deeper periodontal tissues due to plaque accumulation. Key features include bleeding gums, deepening pockets between teeth and gums, and recession or loss of bone. Treatment involves nonsurgical procedures like scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar, as well as potential surgical procedures to reduce deep pockets and regenerate lost bone if nonsurgical methods are not fully effective. Prognosis depends on factors like severity, systemic involvement, remaining teeth and compliance with treatment and maintenance.