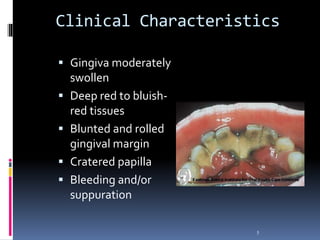
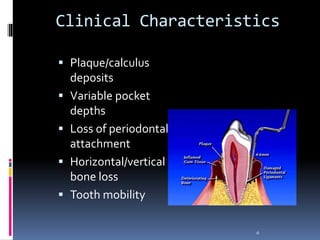
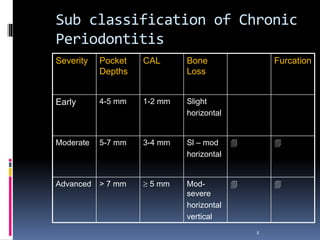
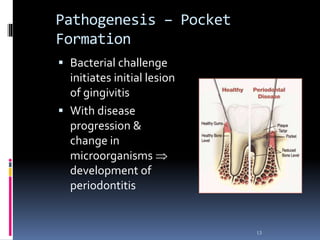
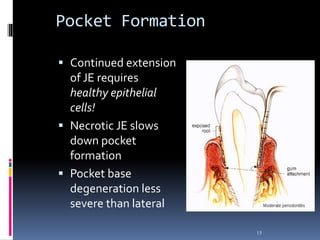
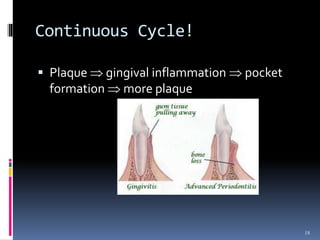
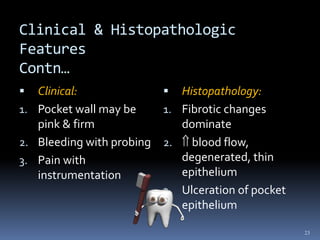
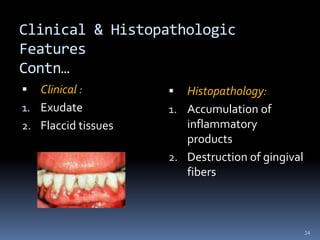
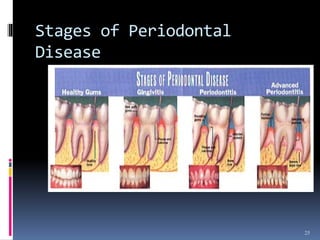
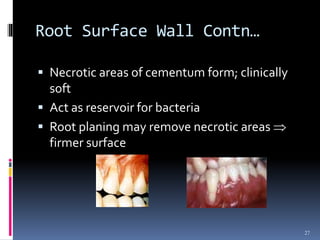
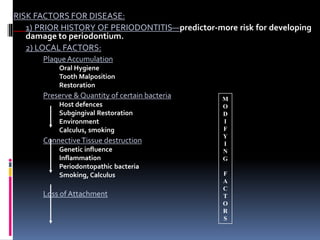
Chronic periodontitis is a slowly progressive infectious disease that results in inflammation of the gums and bone destruction around the teeth. It is caused by a subgingival biofilm of bacteria that spreads below the gumline. Common symptoms include bleeding gums, deepening pockets between teeth, and loose or mobile teeth. Treatment involves nonsurgical procedures like scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar, as well as surgery in some cases to regenerate lost bone and reduce pocket depths. Prognosis depends on factors like patient compliance, systemic health issues, disease severity, and tooth-specific characteristics such as attachment levels and furcation involvement.