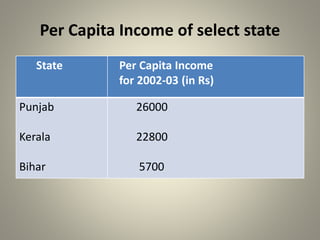
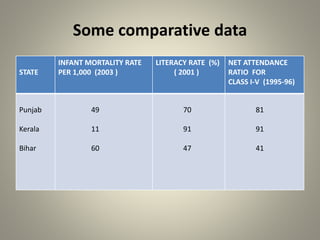
Development can be understood in different ways by different people as they may have varying goals. While income is important, people also desire non-material goals around freedom, security, and respect. National development aims to improve standards of living across a population but must consider more than just income, and development goals and measures also vary between individuals and communities. Assessing development requires looking at multiple factors like health, education, and access to resources, rather than only economic measures like income which do not ensure things like clean environment and healthcare. Long term development also needs consideration of sustainability of resources and environment.