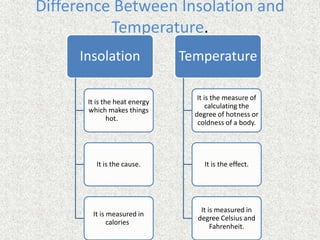
The document discusses solar radiation and the processes that control Earth's heat balance and temperature distribution. It explains that Earth receives energy from the sun which is absorbed and radiated back to space. Some key points are:
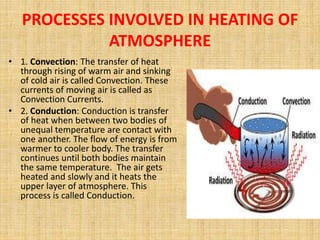
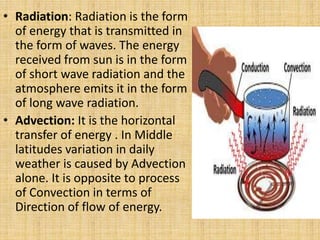
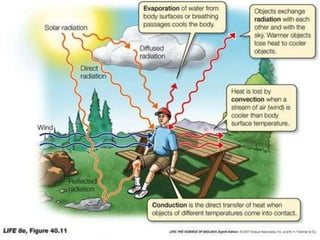
- Solar radiation heats the atmosphere through various processes like convection, conduction, and radiation.
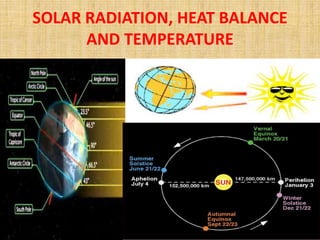
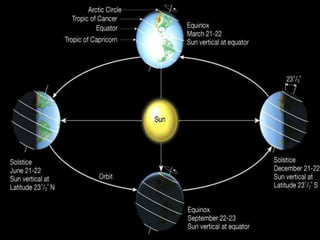
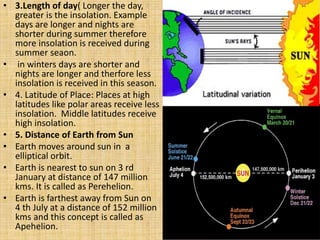
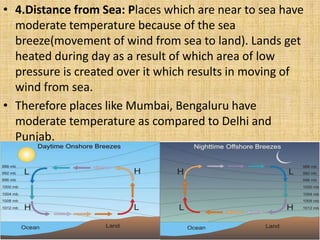
- Factors like the Earth's rotation, revolution, latitude, proximity to oceans influence the amount of incoming solar radiation (insolation) at different locations.
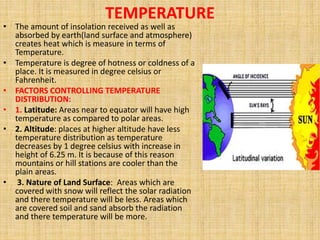
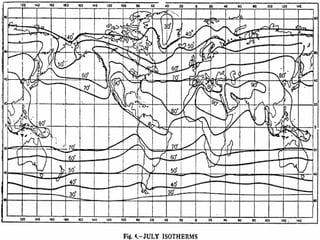
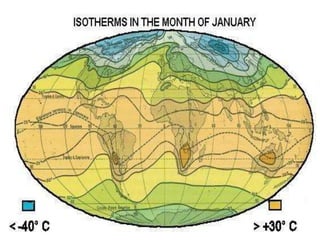
- Earth's temperature is determined by the balance between the solar energy received and radiated back to space. Temperature varies based on latitude, altitude, land/sea distribution and ocean/wind currents.