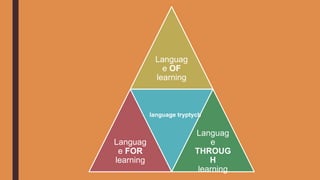
CLIL (Content and Language Integrated Learning) is an approach that integrates teaching academic content with the teaching of a non-native language. It has 4 guiding principles and involves 5 stages: building a shared vision, reflecting the context, focusing on content, communication, cognition and culture, providing resources, and monitoring/evaluating. The methodology creates a safe environment for active, peer-cooperative learning with scaffolding. Teachers act as facilitators and provide authentic input while students use their background knowledge to participate and apply new content knowledge.