1) The document outlines a course on Cleaner Production Techniques, including the course details, outline, and evaluation procedure.
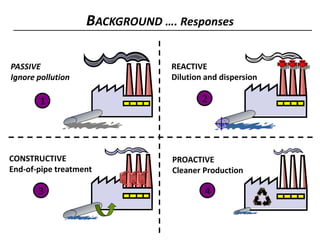
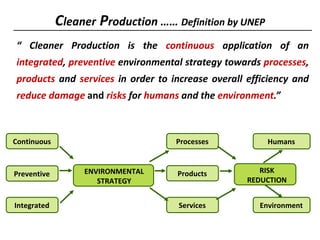
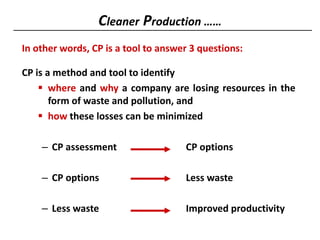
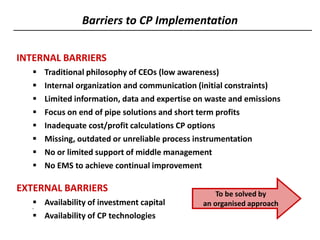
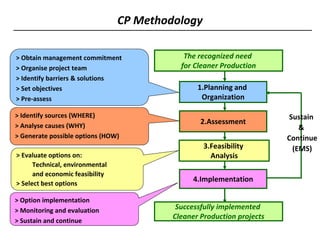
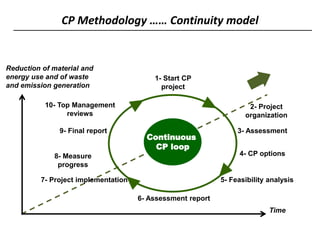
2) It then provides an overview of cleaner production, defining it as a preventative environmental strategy to increase efficiency and reduce risks. It discusses cleaner production principles and how it can identify ways to minimize waste and pollution.
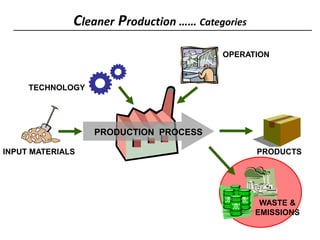
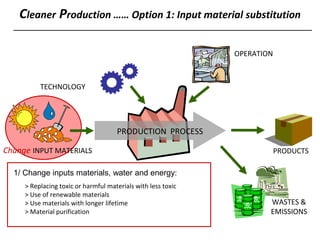
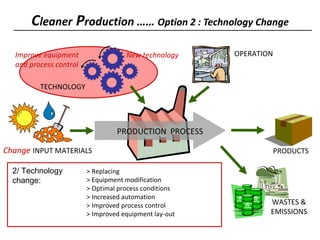
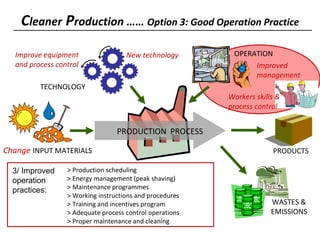
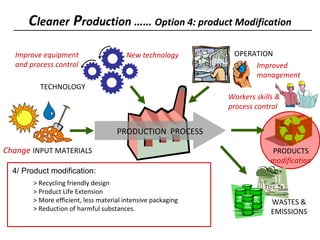
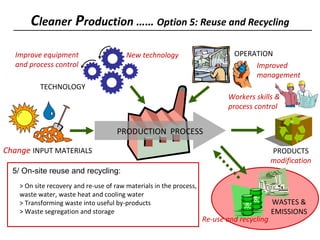
3) The document lists 5 categories of cleaner production options: input material substitution, technology changes, improved operations, product modifications, and reuse/recycling. It provides examples of options within each category.