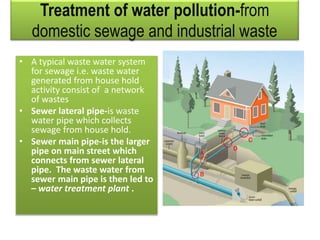
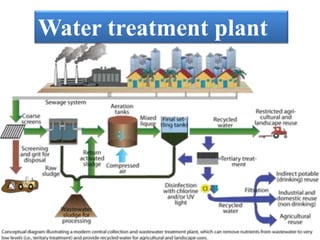
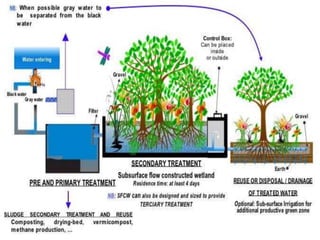
This document discusses sources and impacts of industrial water pollution. It notes that industrial waste from sources like steel, food, and chemical industries introduces pollutants like heavy metals, acids, alkalies, oils, and petrochemicals into water bodies. These pollutants can harm aquatic life and contaminate fish. The document also examines offshore oil drilling as a source of water pollution through drilling fluids, oil spills, and other discharges. Oil pollution damages marine organisms and can disrupt food chains. Proper environmental assessment and use of biodegradable drilling fluids can help control pollution from offshore drilling.

![SOURCES
• it is caused by emission of
industrial waste [effluent] into
water bodies. It is the main source
–of water pollution
• Industrial waste includes organic
pollutants &toxic chemical. i.e
heavy metals
• Acid & alkalies
• Oils,lubricant,petroleum &grease
• Industrial waste enters from-
• Iron & steel industry
• Food industry
• Mines
• Organic chemical industries –
which includes paints
,dyes,pesticides,detergents,paper
etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryppt-150518094016-lva1-app6891/85/Industrial-waste-2-320.jpg)



![IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY
• Conservation of iron to
steel , contaminates
waste water with –
hydraulic oils. Treating
iron & steel products
for galvanizing [coating
with zinc] or chromium
plating results in acidic
rinse waters in waste
waters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryppt-150518094016-lva1-app6891/85/Industrial-waste-6-320.jpg)