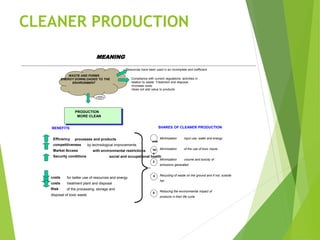
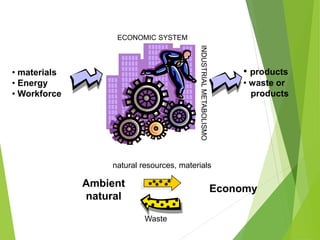
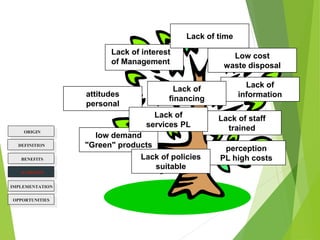
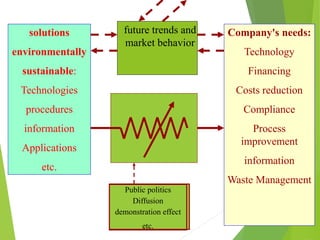
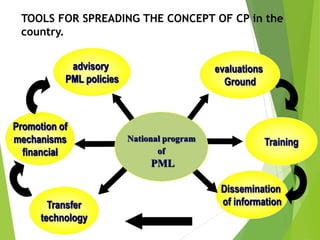
Cleaner Production is a strategy for environmental and business management that aims to efficiently use raw materials and reduce emissions, waste, and risks to human health and the environment. It seeks to encourage cleaner production in industries through developing regulatory frameworks and providing technical and financial support for cleaner production implementation. The goals are to increase resource efficiency, reduce costs and risks, and improve competitiveness for businesses.