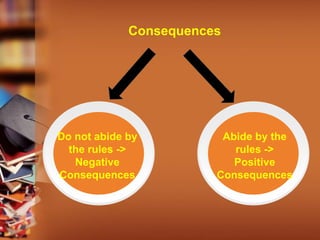
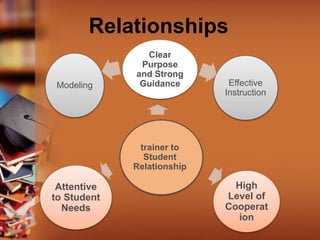
This document provides guidance on effective classroom management strategies for trainers. It discusses the importance of establishing clear rules, procedures and consequences to maintain order and facilitate learning. Different classroom management styles like authoritarian, authoritative, indifferent and laissez-faire are described. Building positive relationships with students and engaging in consistent, well-planned instruction are emphasized as key components of classroom management. Specific tips are offered such as preparing the classroom environment in advance, using assertive body language, maintaining high expectations, and giving students quiet activities to do when finished with their work. Overall, the document stresses the significance of classroom management for trainers to develop a cooperative learning environment.