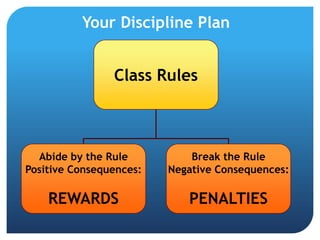
This document provides guidance on effective classroom management strategies for teachers. It discusses establishing clear rules and consequences, preparing engaging lessons, maintaining organized routines and transitions, and gaining parental support. The key aspects of classroom management include having an effective discipline plan with rewards for positive behavior and penalties for misconduct, as well as establishing consistent procedures and routines to minimize disruptions.