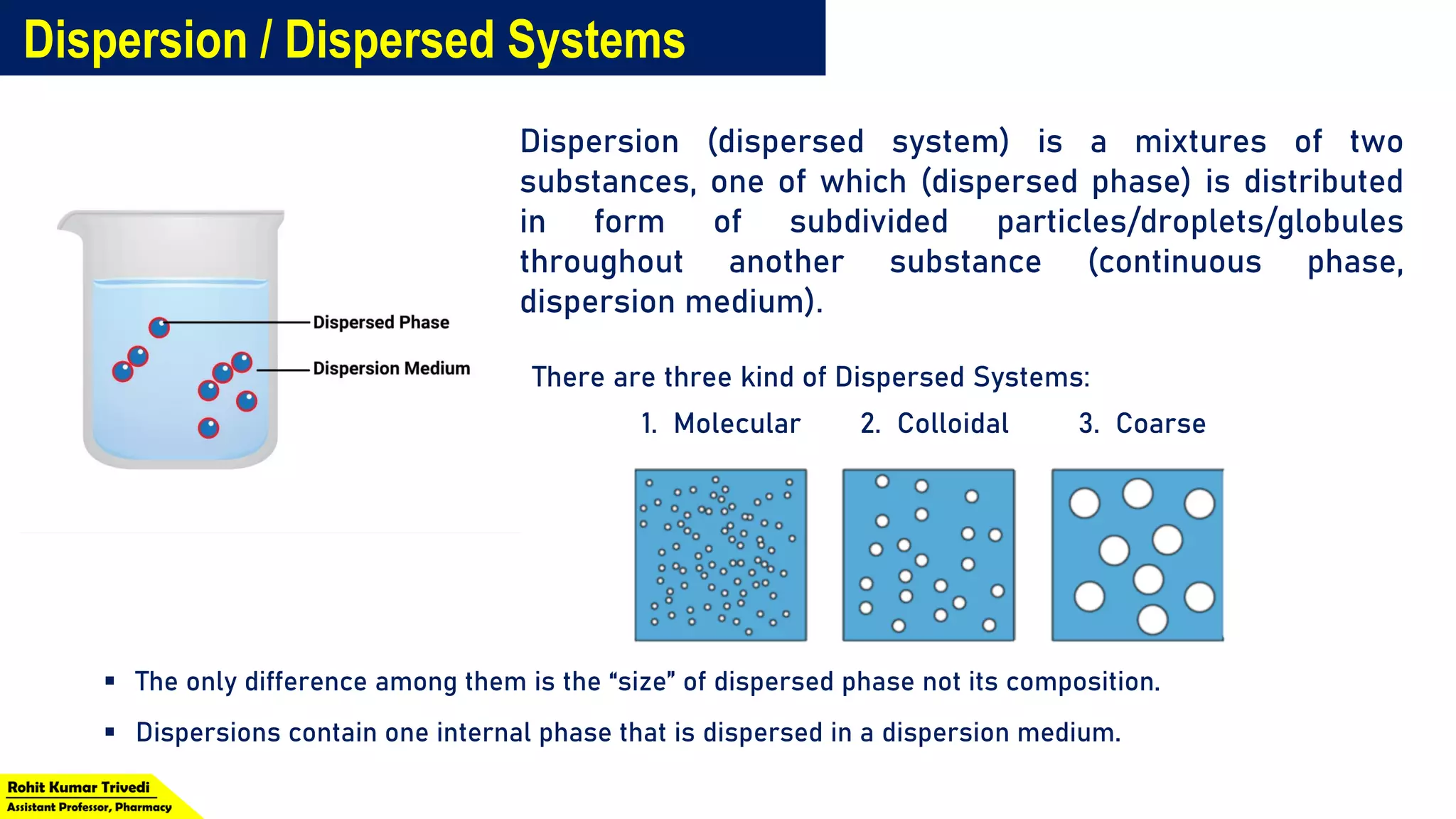
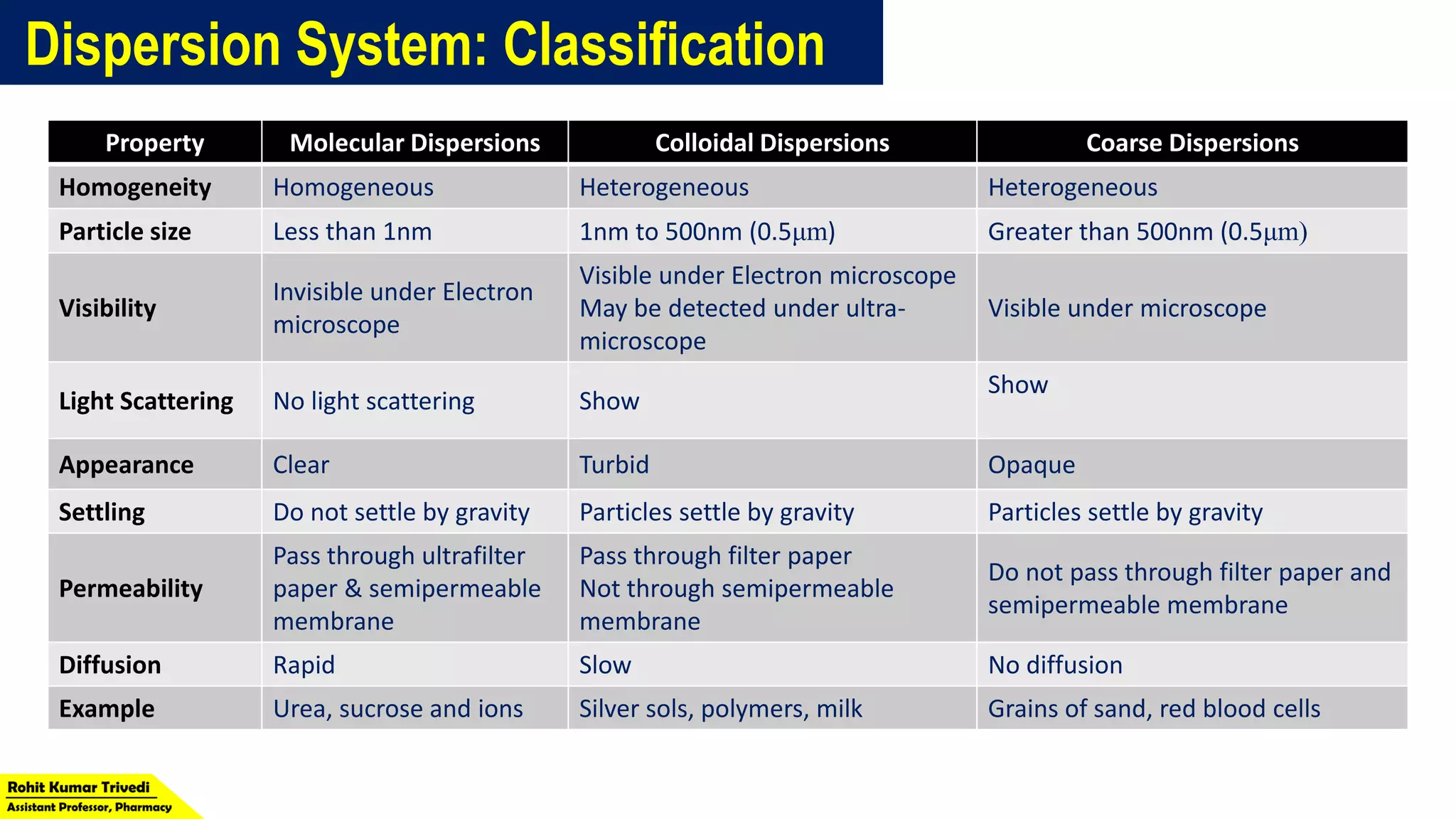
The document discusses the classification of dispersed systems in physical pharmacy, identifying three types: molecular, colloidal, and coarse dispersions, distinguished by the size of the dispersed phase. It outlines their properties, including homogeneity, visibility, light scattering, settling behavior, permeability, and diffusion rates. Examples of each type are provided, such as urea for molecular dispersions and grains of sand for coarse dispersions.