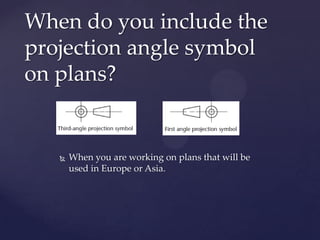
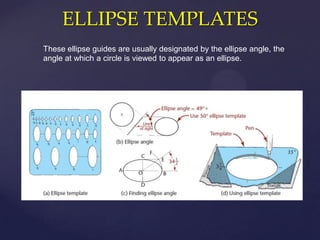
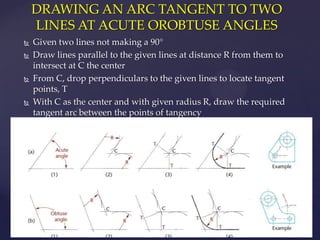
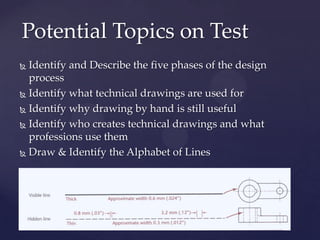
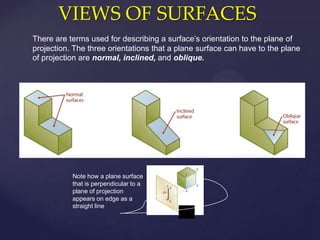
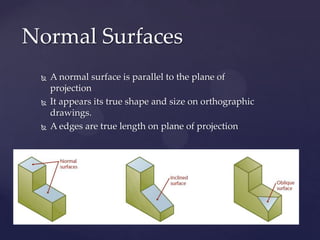
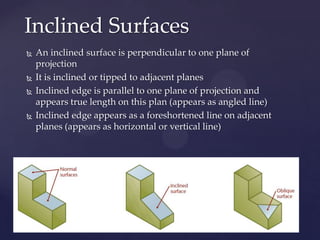
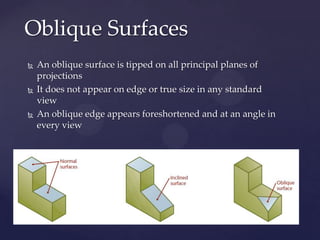
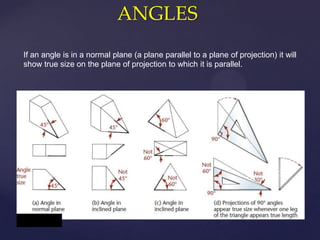
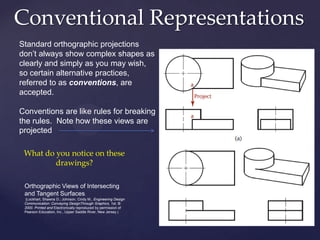
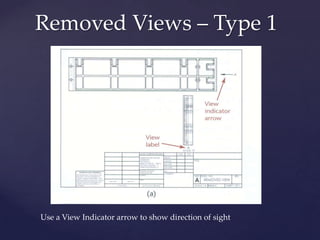
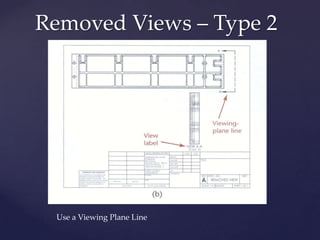
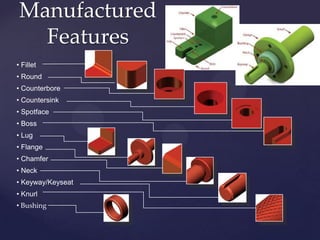
This document provides information about a 2D Essentials class taught by Laura Gerold. The class includes four sections with start and end dates of January 18, 2012 to May 16, 2012. The document then provides questions from students and answers from the instructor on topics that will be covered in the class, including when to include projection angles, how to draw ellipses using foci, drawing arcs tangent to lines, and a test review with potential topics.