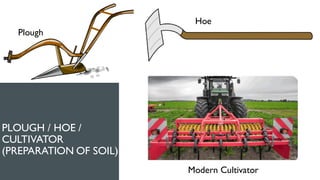
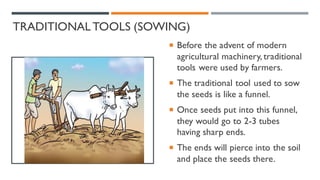
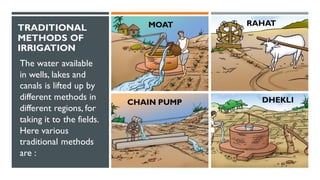
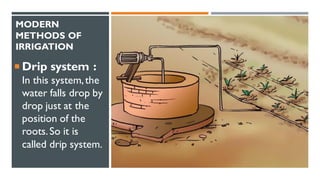
The document discusses crop production and management, highlighting the importance of food for living organisms and the methods required for efficient agricultural practices. It categorizes crops into kharif (sown in the rainy season) and rabi (grown in the winter season) and outlines the basic practices of crop production, including soil preparation, sowing, irrigation, weeding, harvesting, and storage. Additionally, it contrasts traditional and modern agricultural methods and emphasizes the significance of managing both crops and livestock.