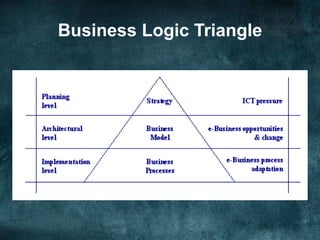
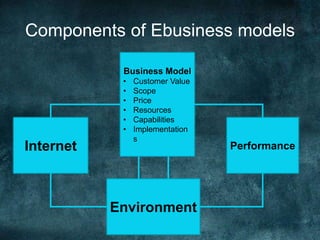
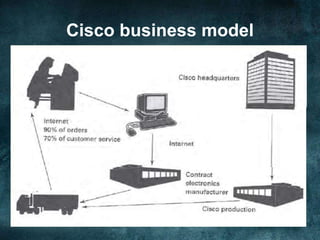
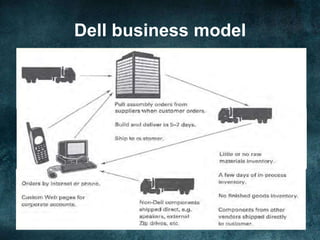
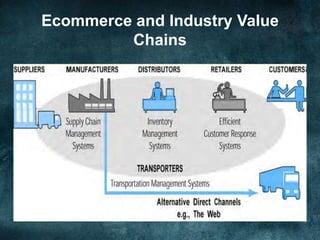
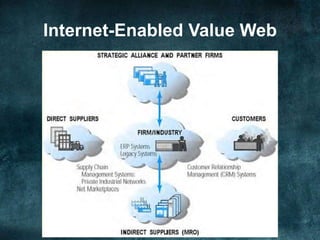
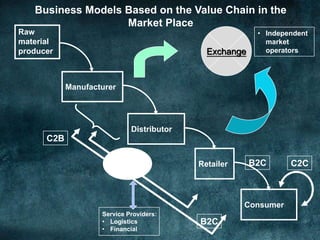
The document discusses various business models and revenue models for e-commerce. It describes common e-business models like the storefront model, auction model, portal model, and dynamic pricing models. It also outlines several revenue models including advertising, affiliate marketing, licensing, subscriptions, transaction fees, and sales. Finally, it examines how the internet impacts industry value chains by increasing efficiencies and enabling new participants like independent market operators and service providers.