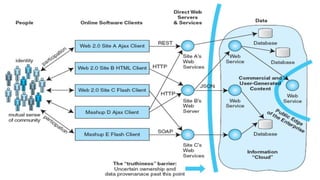
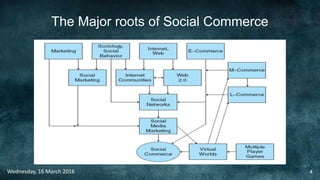
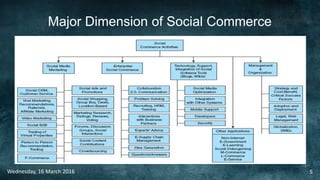
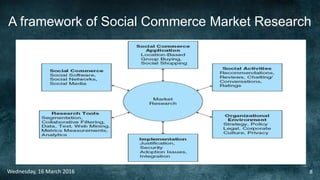
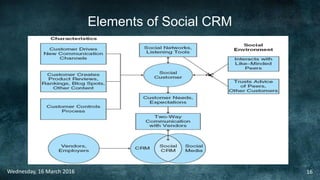
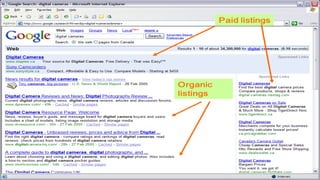
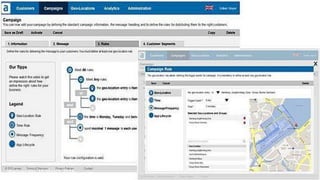
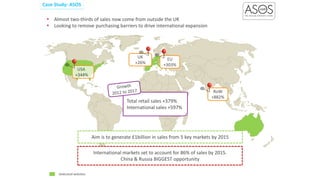
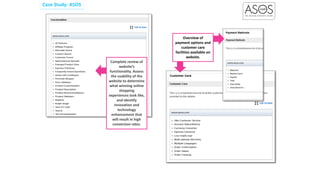
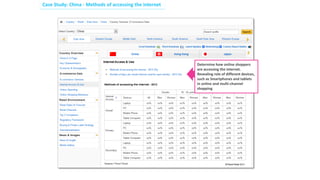
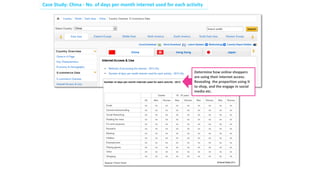
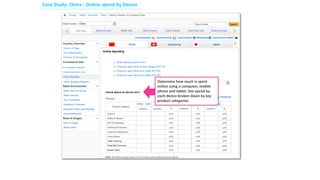
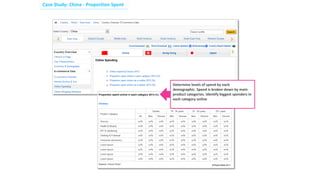
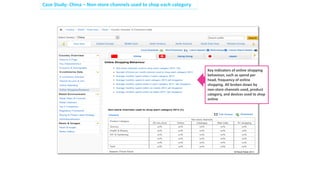
Social commerce refers to e-commerce activities and transactions conducted through social networks or via social media. This document discusses several concepts related to social commerce including social capital, social media marketing, social graphs, social shopping, social advertising, social customer relationship management, crowdsourcing, collective intelligence, location-based advertising and social networks, and location-based services. It also provides case studies on the online retailer ASOS and its operations in China to illustrate examples of social commerce strategies and analytics.