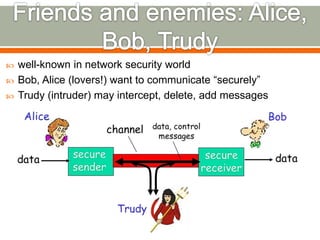
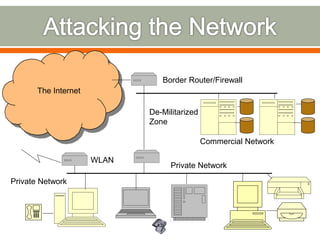
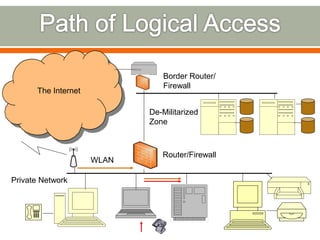
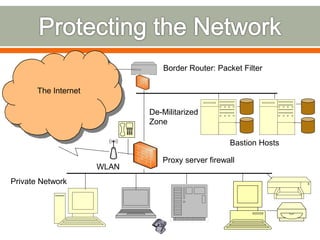
The document discusses various topics related to network security including definitions of network security, common security goals of confidentiality, authentication, integrity and availability, common security threats from attackers, examples of systems and organizations that require network security protections, descriptions of firewalls and their purpose in restricting access between networks, and examples of security attacks like dictionary attacks, denial of service attacks, and evolving cyber threats.