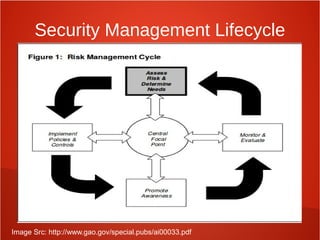
This document discusses information security governance and risk management. It covers several topics:
- The roles and responsibilities of various information security positions such as the security officer, system administrators, and end users.
- Security policies, standards, procedures, and frameworks that organizations can implement to formalize security practices.
- Compliance with regulations and how to map different compliance frameworks.
- Managing risks from third parties, acquisitions, and other organizational changes.
- Ensuring proper information security governance through activities like risk analysis, security awareness training, and oversight from executive management.