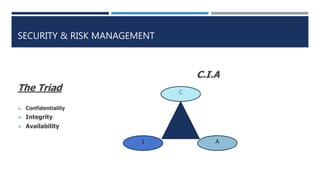
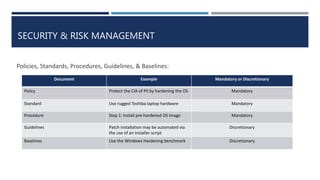
The document provides a comprehensive overview of security and risk management, emphasizing the importance of confidentiality, integrity, and availability in the protection of information assets. It discusses governance frameworks, compliance with laws, and best practices for business continuity and disaster recovery planning. Additionally, it highlights the role of ethical considerations and the significance of a structured approach to developing and implementing security policies.