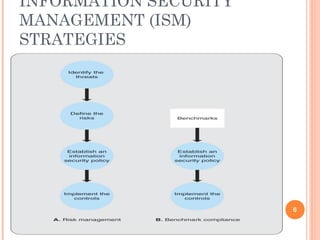
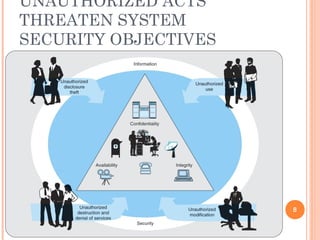
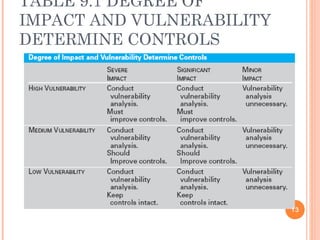
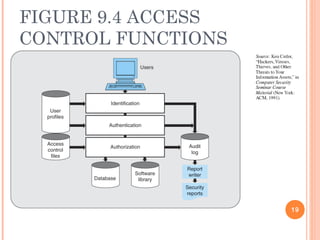
The document outlines the critical aspects of information security and management, touching on the need for security measures, the balance between security and individual rights, and key objectives such as confidentiality, availability, and integrity. It discusses various threats, risk management strategies, and the importance of business continuity management. Additionally, it covers technical and formal controls, industry standards, and the necessity for professional certification in the field.