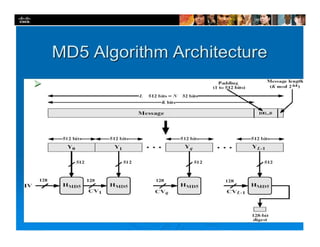
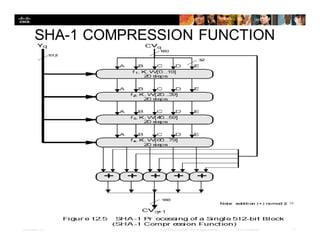
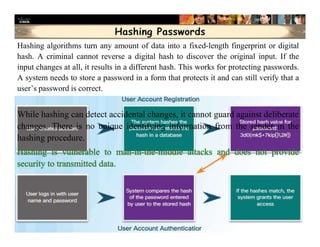
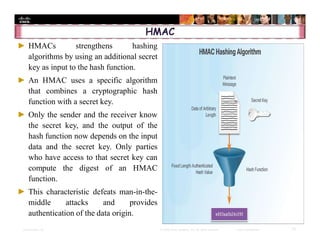
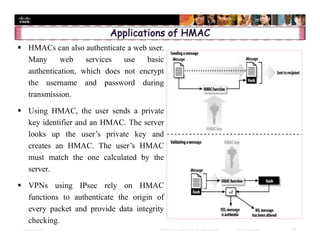
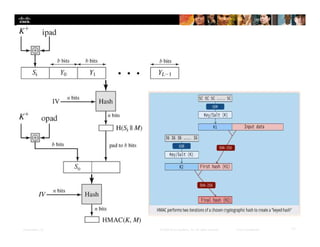
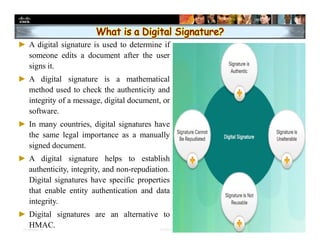
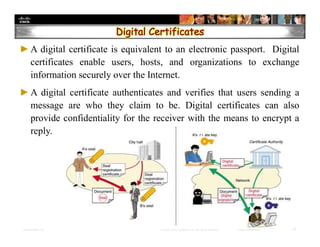
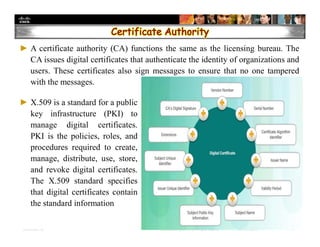
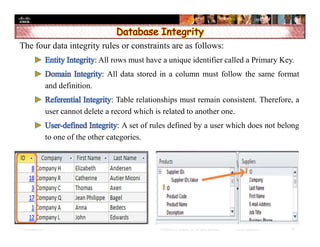
The document focuses on ensuring data integrity through various methods such as hashing, digital signatures, and digital certificates. It explains the importance of these methods in authenticating data, detecting alterations, and maintaining database integrity. Key concepts include hashing algorithms, salting, the role of certificate authorities, and validation rules for data input.