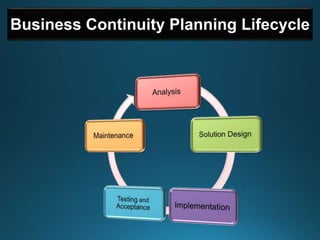
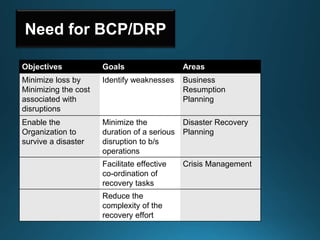
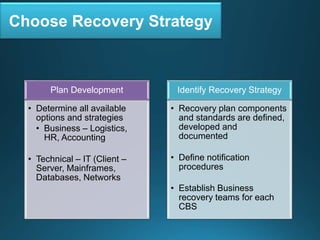
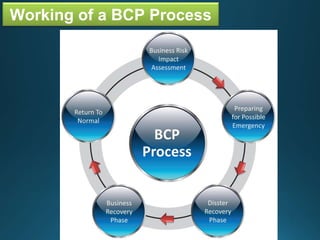
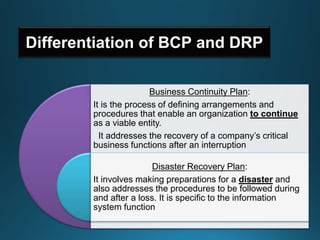
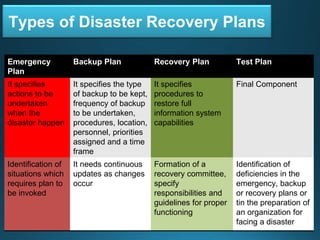
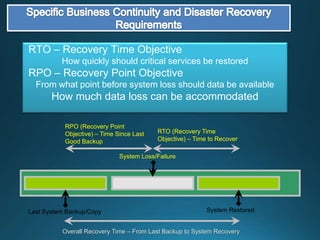
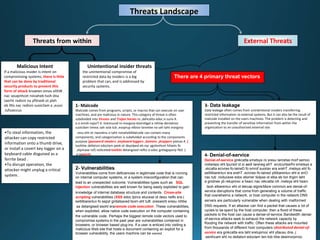
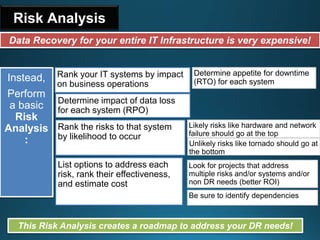
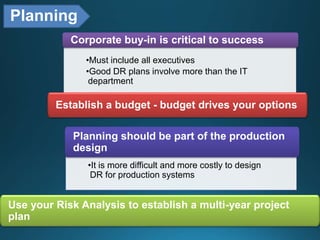
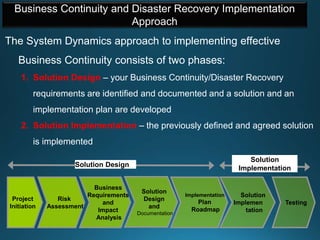
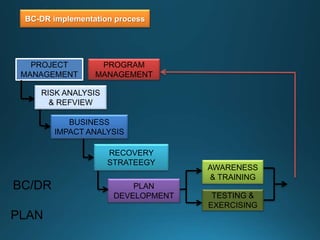
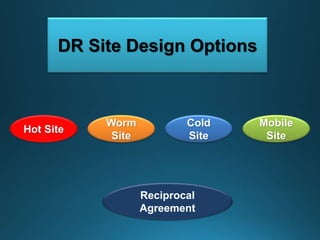
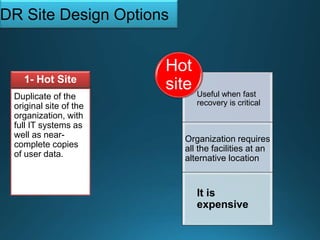
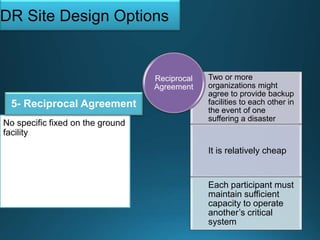
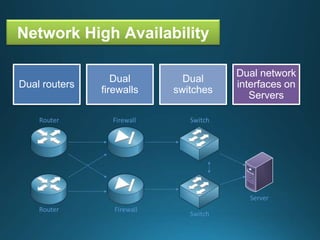
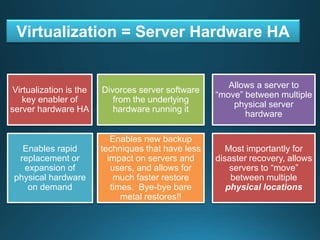
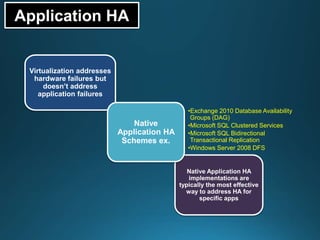
Business continuity planning involves creating a logistical plan for how an organization will recover from a disaster in a predetermined time. Disaster recovery planning addresses procedures for recovering critical business functions after an interruption. The document discusses business continuity planning lifecycles, objectives of business continuity and disaster recovery plans, developing and testing plans, differentiating business continuity and disaster recovery plans, types of backups and disaster recovery plans, recovery time objectives and recovery point objectives, threats to organizations, and risk analysis and planning considerations.