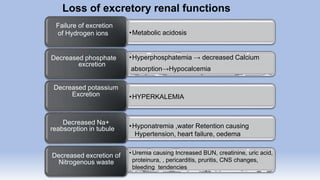
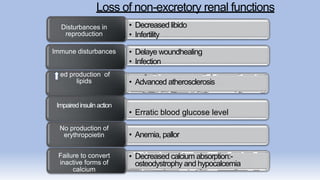
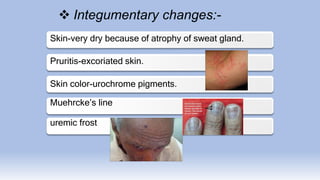
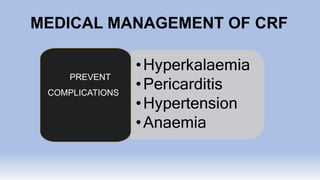
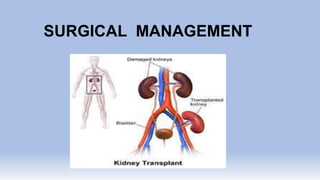
The document provides information on chronic renal failure (CRF), also known as chronic kidney disease. It defines CRF as a progressive deterioration of renal function resulting in the body's inability to maintain fluid, electrolyte and waste product balance. Causes include diabetes, hypertension, kidney infections, injuries, certain medications, and hereditary conditions. Symptoms affect multiple body systems and include fatigue, edema, neurological changes, and susceptibility to infection. Treatment involves managing complications through medications, dietary modifications, dialysis, and in some cases, surgery. Nursing care focuses on monitoring for fluid overload, maintaining nutrition, managing symptoms, and educating patients and their families about CRF and treatment.