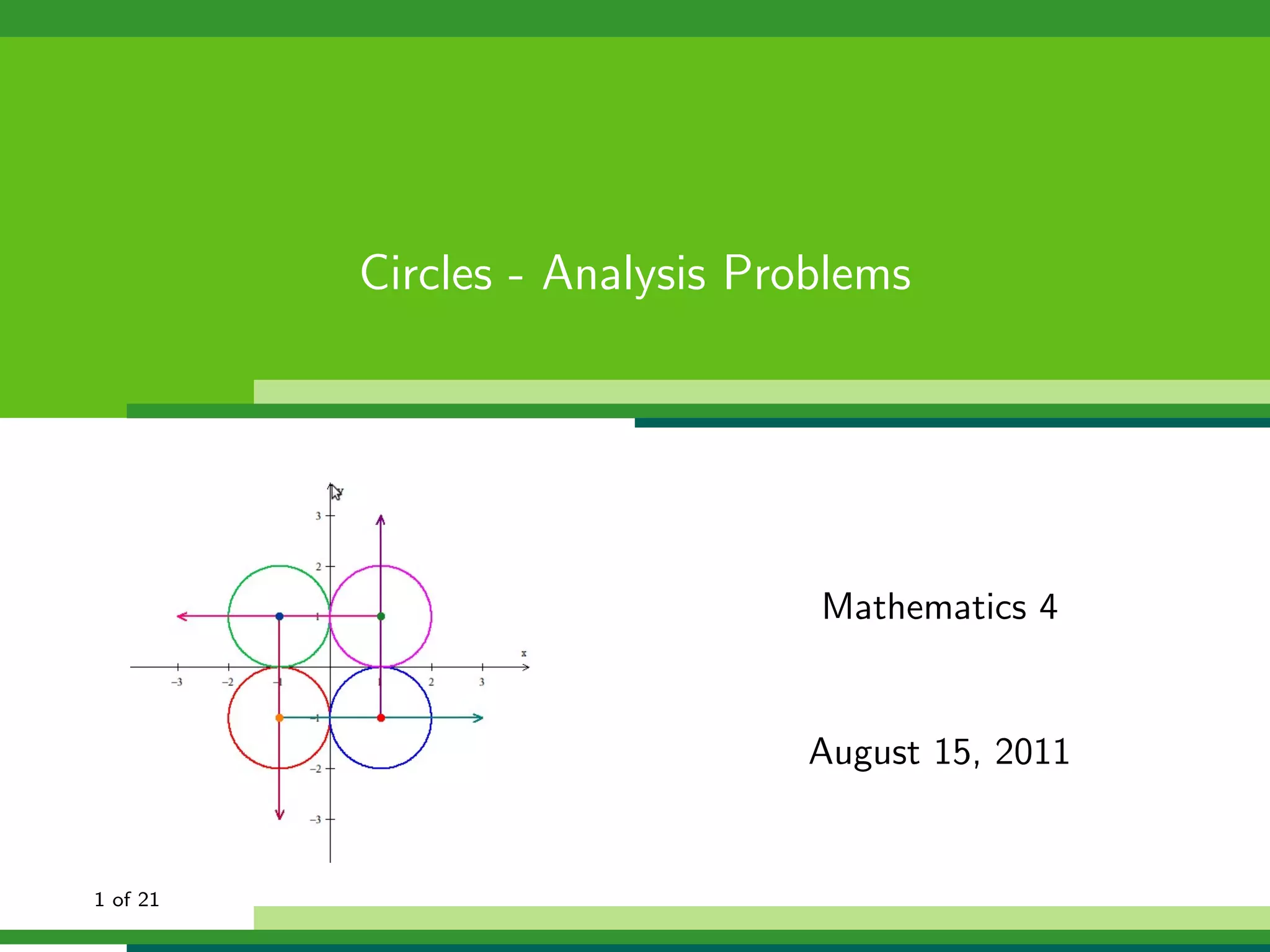
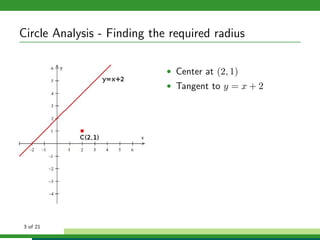
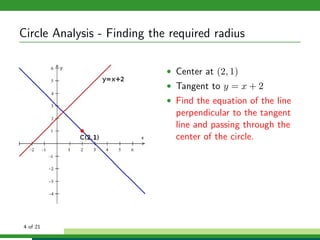
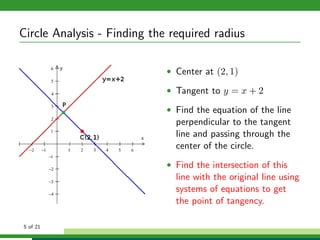
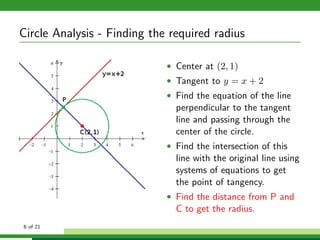
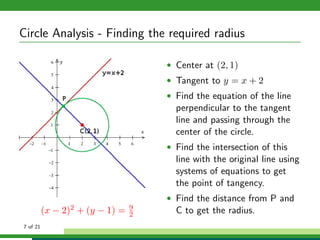
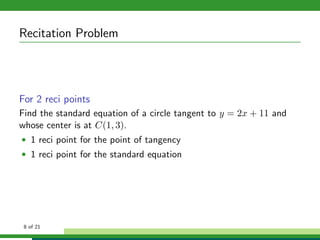
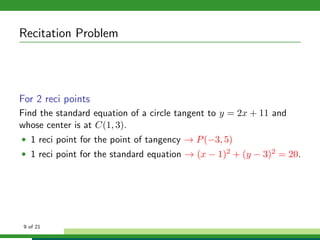
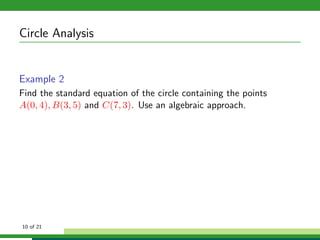
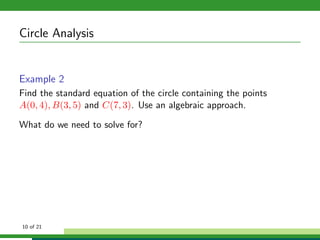
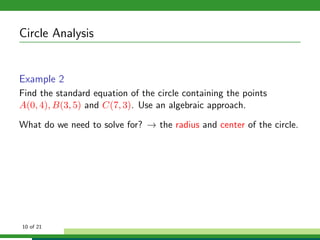
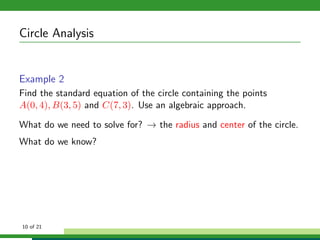
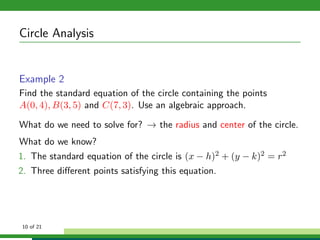
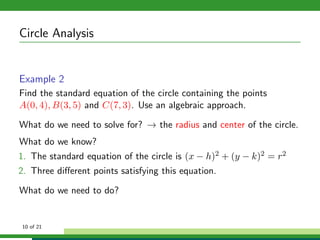
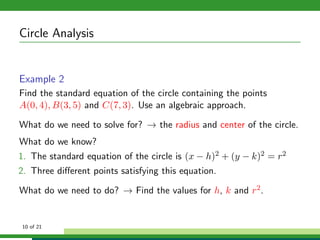
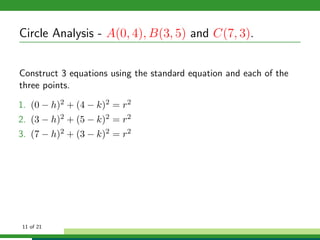
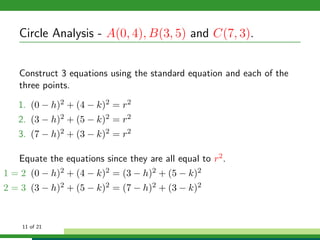
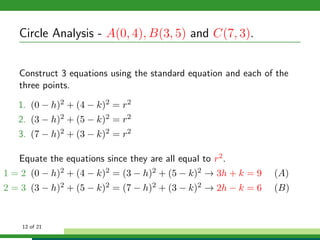
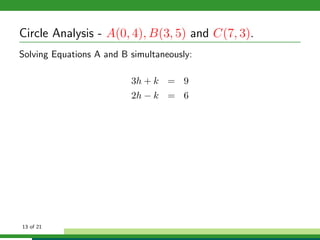
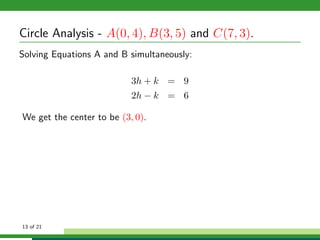
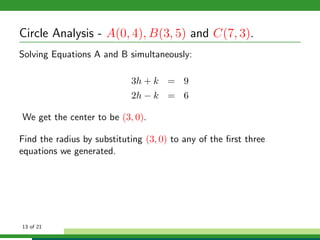
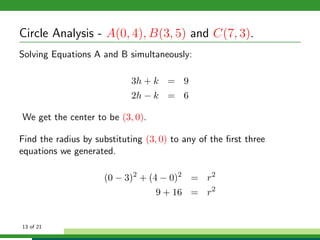
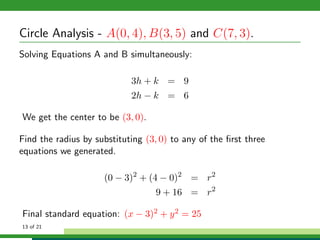
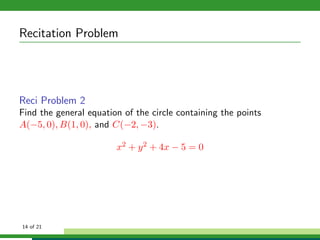
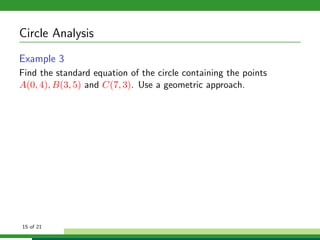
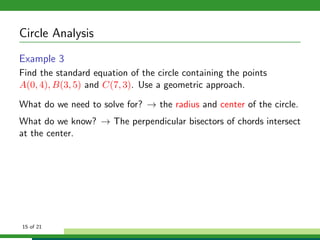
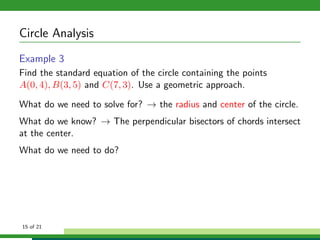
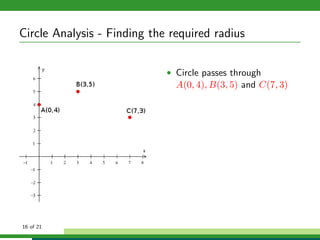
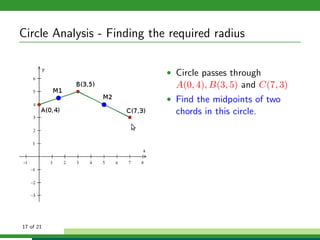
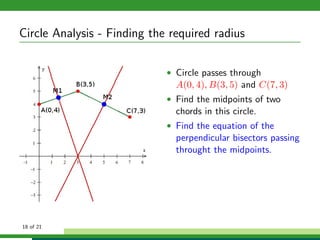
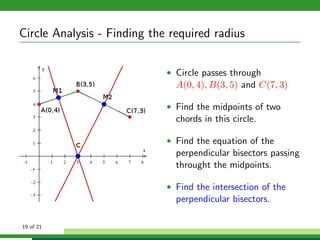
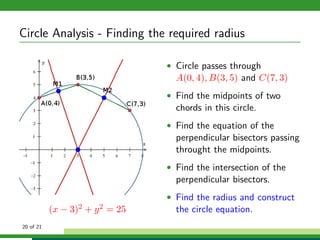
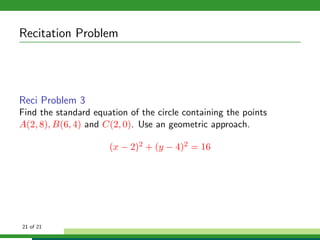
This document provides examples and explanations for analyzing problems involving circles. It begins by working through an example of finding the equation of a circle tangent to a given line with a specified center. It then discusses using an algebraic approach to find the standard equation of a circle passing through three given points by setting up three equations and solving simultaneously for the center and radius. Finally, it covers using a geometric approach involving finding the perpendicular bisectors of chord midpoints and their intersection to determine the circle's center. The document aims to demonstrate different methods for solving circle geometry problems.