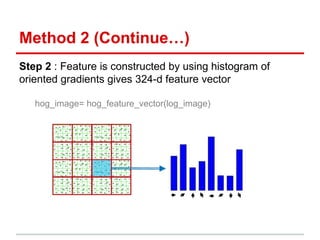
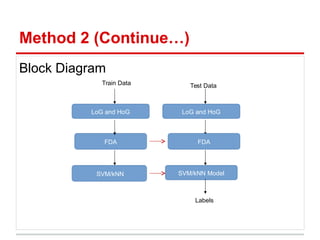
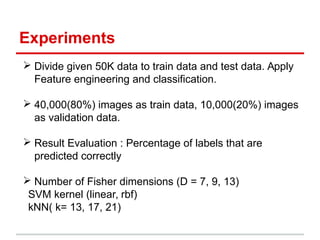
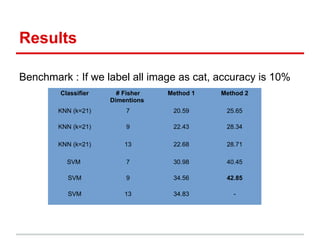
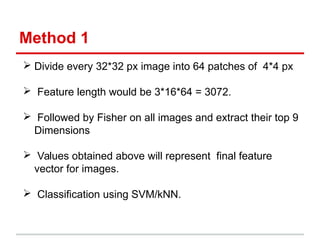
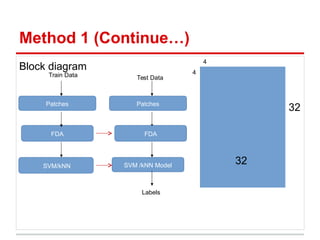
This document describes the CIFAR-10 dataset for classifying images into 10 categories. It contains 60,000 32x32 color images split into 50,000 training and 10,000 test images. Two methods are proposed: Method 1 extracts patches and features from each image and uses SVM/kNN, while Method 2 uses LoG and HoG features to preserve shape before SVM/kNN classification. Experiments test different parameters, with the best accuracy around 42% using a 13-dimensional Fisher vector and RBF SVM kernel.





![Method 2
Aim : Preserve the Shape of Image
Step 1 : Image is filtered using Laplace of Gaussian
filter(LoG).
log_image = edge(gray_image,'log', [], 2);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/patternfinders-141205004957-conversion-gate02/85/CIFAR-10-9-320.jpg)